Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>
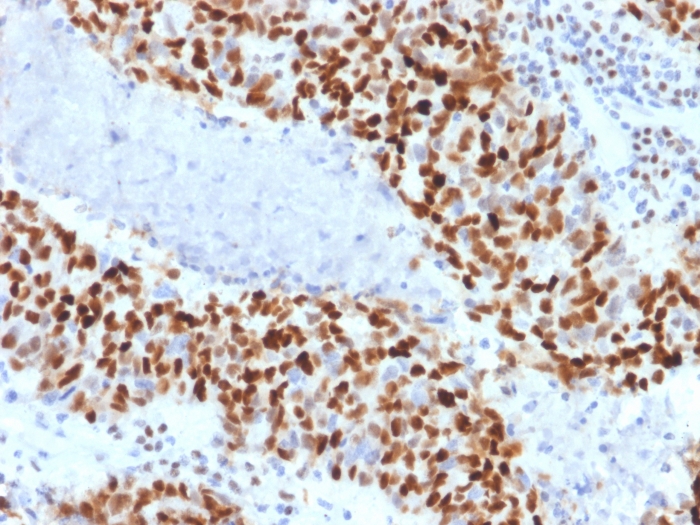
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human colon carcinoma stained with Cyclin E Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CCNE1/2460).
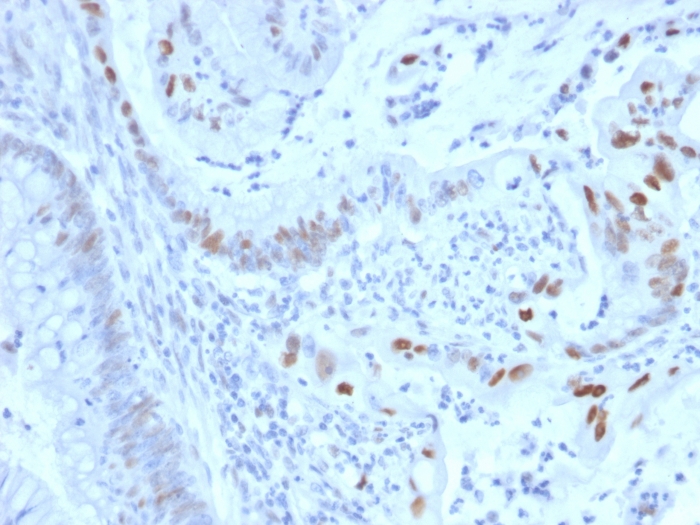
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human colon carcinoma stained with Cyclin E Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CCNE1/2460).
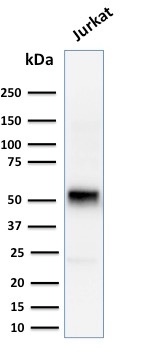
Western Blot Analysis of human Jurkat cell lysate using Cyclin E Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CCNE1/2460).
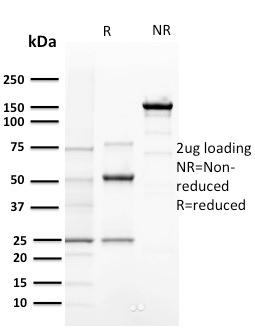
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified Cyclin E Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CCNE1/2460). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
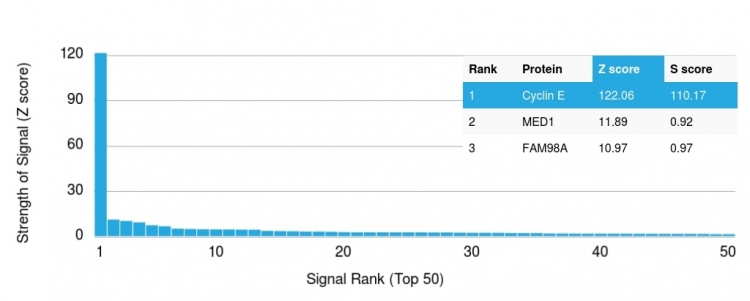
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using Cyclin E Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CCNE1/2460). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
Cyclin E belongs to the highly conserved cyclin family, whose members exhibit distinct expression and degradation patterns which contribute to the temporal coordination of each mitotic event. Cyclins function as regulators of CDK kinases. Cyclin E forms a complex with and functions as a regulatory subunit of CDK2, whose activity is required for cell cycle G1/S transition. Cyclin E accumulates at the G1-S phase boundary and is degraded as cells progress through S phase. Cyclin E overexpression has been observed in many tumors, which results in chromosome instability, and thus may contribute to tumorigenesis.
There are no reviews yet.