Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>
Macrophages are a type of white blood cell that are an essential part of the immune system. They play a crucial role in innate and adaptive immunity and are involved in various functions, including phagocytosis, antigen presentation, and the secretion of inflammatory molecules. Macrophages are found in tissues throughout the body and are particularly important for defending against infections and maintaining tissue homeostasis.
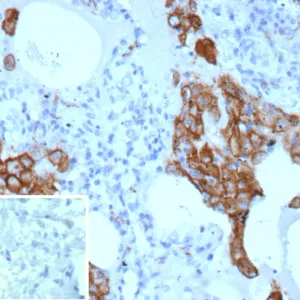
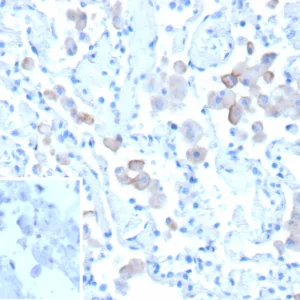
Macrophage identification and the quantification of macrophage biomarkers allow for the characterization of these immune cells under various physiological and pathological contexts, aiding in the understanding of immune responses, disease mechanisms, and the development of potential therapies. Macrophage protein biomarkers provide information about the activation state (M1 vs. M2) state of these cells to understand their role in inflammation and immune responses. Some biomarkers yield prognostic information about disease outcomes and can predict cancer aggressiveness. Furthermore, macrophage biomarkers are relevant to developing immunotherapies or treatments targeting macrophages, such as therapies for cancer or inflammatory conditions,
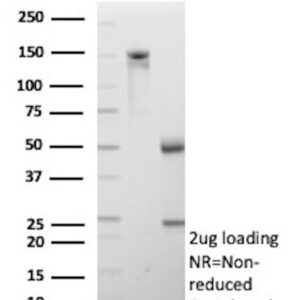
The choice of which macrophage cell biomarkers to measure depends on the specific goals of the analysis and the research context. NeoBiotechnologies offers a variety of validated antibodies targeting macrophage cell protein biomarkers that are guaranteed to yield accurate and reliable results. A list of our specific and sensitive antibodies and their intended applications is shown in the table below.
Showing all 3 results
Showing all 3 results