Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>
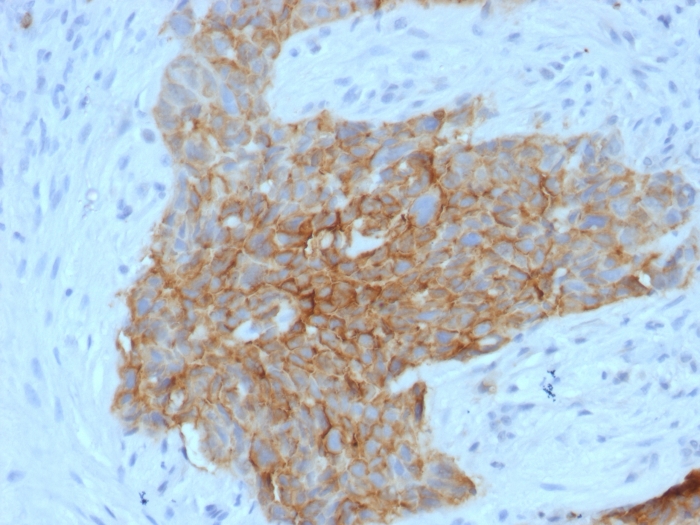
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Tongue stained with GLUT-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GLUT1/2475).
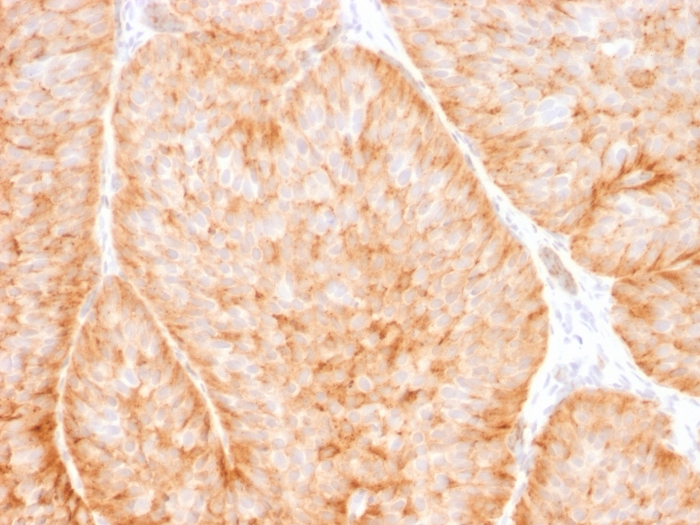
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Bladder carcinoma stained withGLUT-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GLUT1/2475).

SDS-PAGE Analysis Purified GLUT-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GLUT1/2475). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
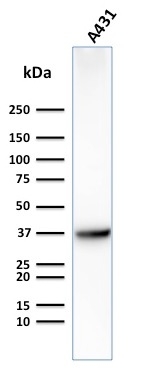
Western Blot Analysis of Human A431 cell lysate using GLUT-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GLUT1/2475).
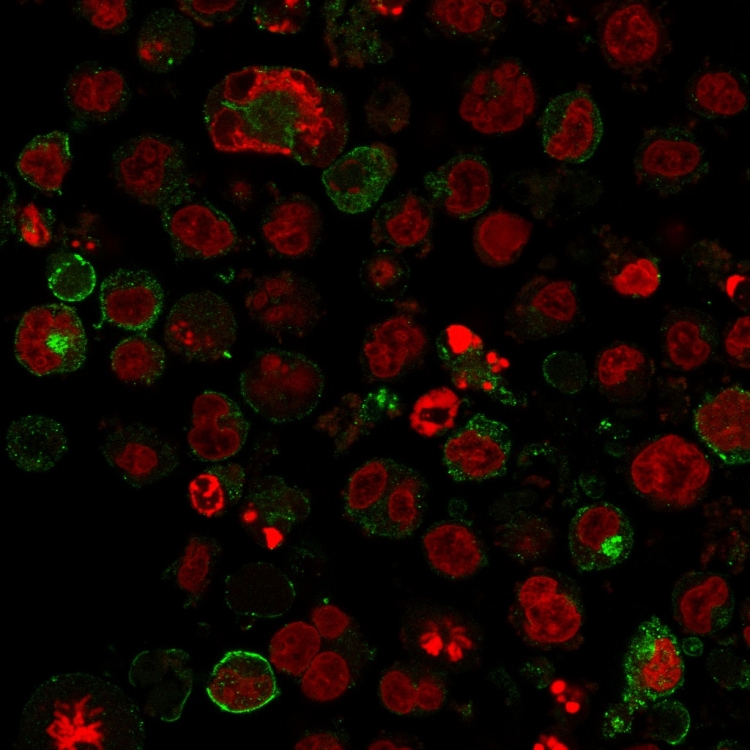
Immunofluorescence staining of K562 cells using GLUT-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GLUT1/2475) followed by goat anti-Mouse IgG conjugated to CF488 (green). Nuclei are stained with Reddot.
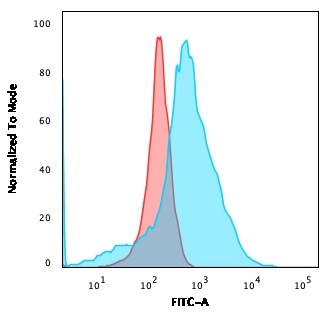
Flow Cytometric Analysis of K562 cells using GLUT-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GLUT1/2475) followed by goat anti-Mouse IgG-CF488 (Blue); Isotype Control (Red).
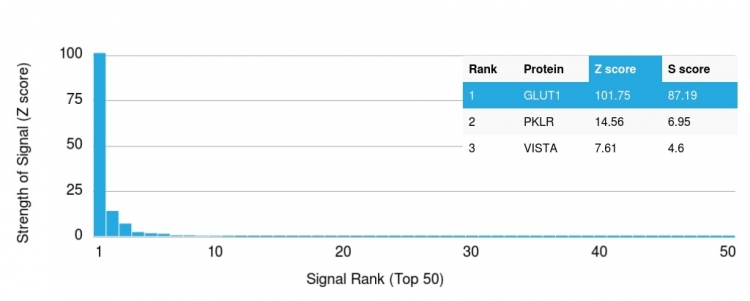
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using GLUT-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GLUT1/2475). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD�s) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD�s) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
Recognizes a protein of 55kDa, which is identified as GLUT-1. Glucose transporters are integral membrane glycoproteins involved in transporting glucose into most cells. There are many types of glucose transport carrier proteins, designated as Glut-1 to Glut-12. Glut-1 is a major glucose transporter in the mammalian blood-brain barrier. It is expressed in high density on the membranes of human erythrocytes and the brain capillaries that comprise the blood-brain barrier. Glut-1 is expressed at variable levels in many human tissues. Overexpression of Glut-1 has been linked to tumor progression or poor survival of patients with carcinomas of the colon, breast, cervical, lung, bladder and mesothelioma. Glut-1 is a sensitive and specific marker for the differentiation of malignant mesothelioma (positive) from reactive mesothelium (negative).
There are no reviews yet.