Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>
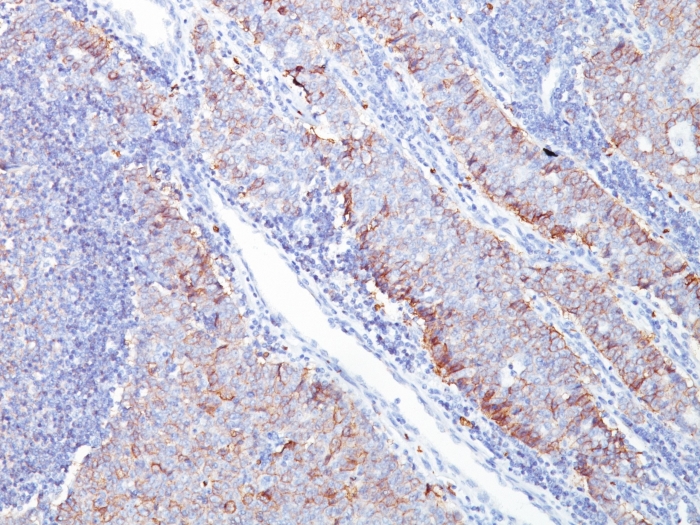
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Breast Carcinoma stained with GLUT-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GLUT1/2476).
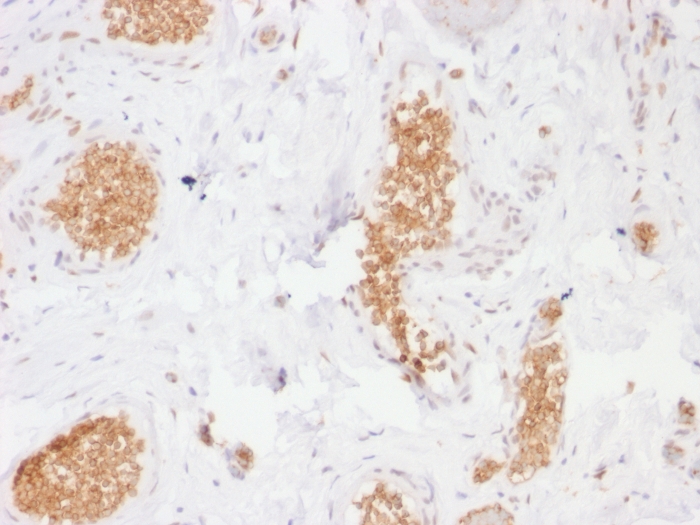
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Bladder stained with GLUT-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GLUT1/2476).
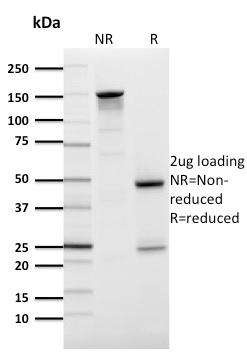
SDS-PAGE Analysis Purified GLUT-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GLUT1/2476). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
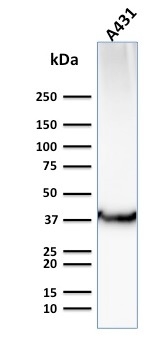
Western Blot Analysis of Human A431 cell lysate using GLUT-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GLUT1/2476).
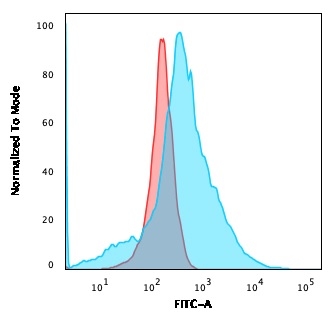
Flow Cytometric Analysis of K562 cells using GLUT-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GLUT1/2476) followed by goat anti-Mouse IgG-CF488 (Blue); Isotype Control (Red).
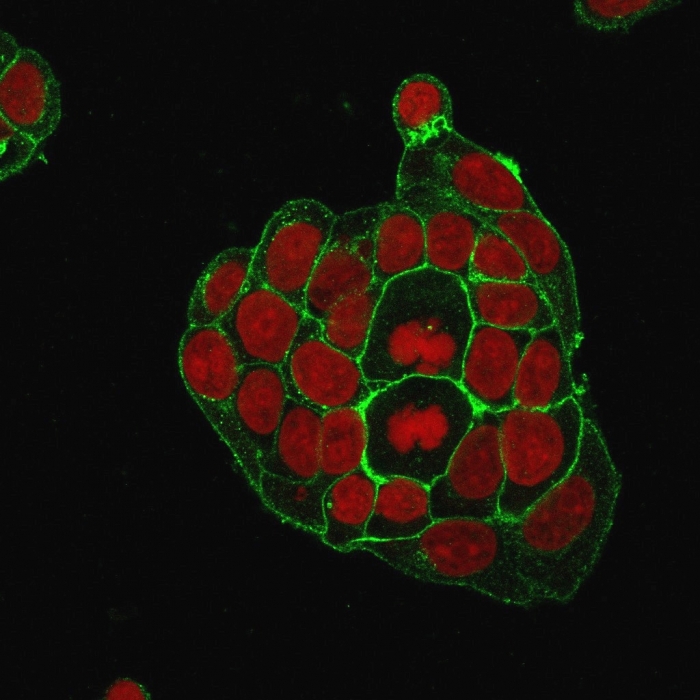
Immunofluorescence staining of MCF-7 cells using GLUT-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GLUT1/2476) followed by goat anti-Mouse IgG conjugated to CF488 (green). Nuclei are stained with Reddot.
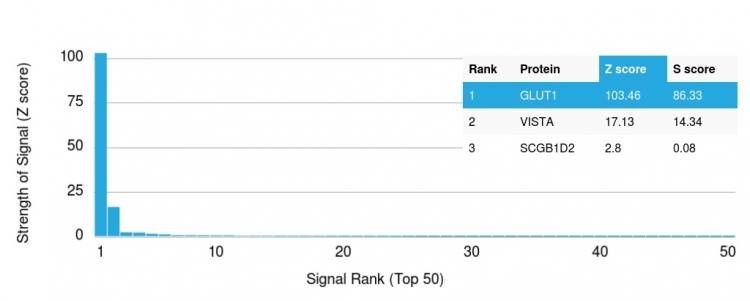
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using GLUT-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GLUT1/2476). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SDs) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SDs) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
Recognizes a protein of 55kDa, which is identified as GLUT-1. Glucose transporters are integral membrane glycoproteins involved in transporting glucose into most cells. There are many types of glucose transport carrier proteins, designated as Glut-1 to Glut-12. Glut-1 is a major glucose transporter in the mammalian blood-brain barrier. It is expressed in high density on the membranes of human erythrocytes and the brain capillaries that comprise the blood-brain barrier. Glut-1 is expressed at variable levels in many human tissues. Overexpression of Glut-1 has been linked to tumor progression or poor survival of patients with carcinomas of the colon, breast, cervical, lung, bladder and mesothelioma. Glut-1 is a sensitive and specific marker for the differentiation of malignant mesothelioma (positive) from reactive mesothelium (negative).
There are no reviews yet.