Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>
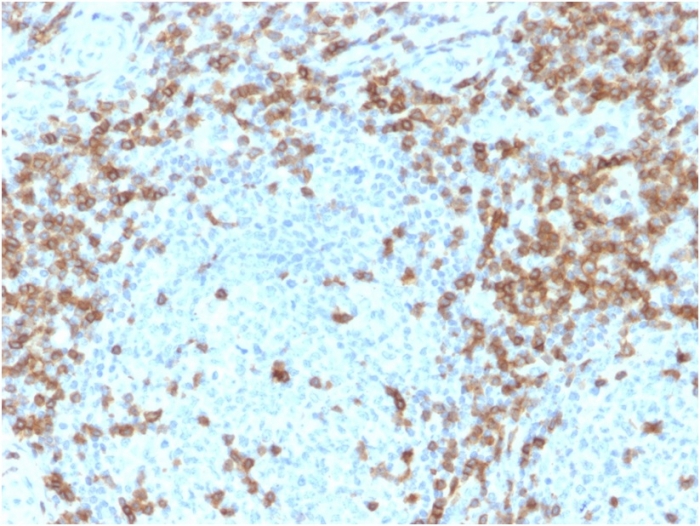
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human tonsil stained with CD5-Monospecific Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CD5/2418). HIER: Tris/EDTA, pH9.0, 45min. 2°C: HRP-polymer, 30min. DAB, 5min.
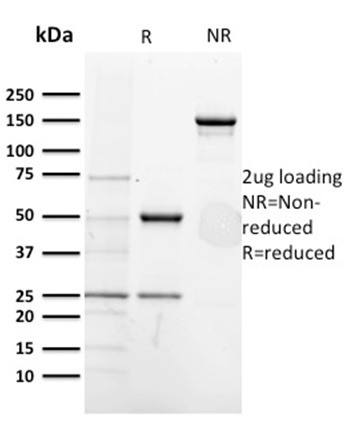
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified CD5-Monospecific Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CD5/2418). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
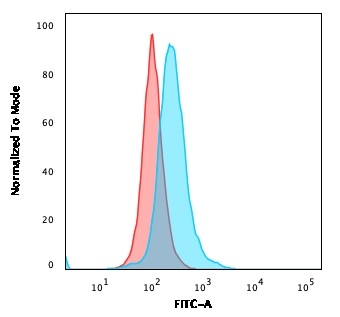
Flow Cytometric Analysis of PFA-fixed Ramos cells. CD5-Monospecific Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CD5/2418). followed by Goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); isotype control (red).

Immunofluorescent staining of PFA-fixed Ramos cells using CD5-Monospecific Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CD5/2418) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (green). Nuclei are stained with RedDot.
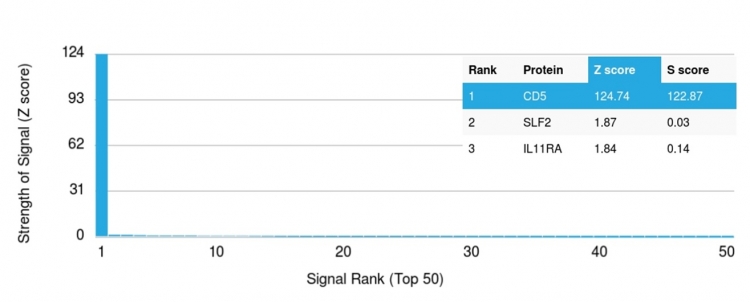
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using CD5-Monospecific Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CD5/2418). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
Recognizes a 67kDa transmembrane protein, which is identified as CD5. The CD5 antigen is found on 95% of thymocytes and 72% of peripheral blood lymphocytes. In lymph nodes, the main reactivity is observed in T cell areas. Anti-CD5 is a pan T-cell marker that also reacts with a range of neoplastic B-cells, e.g. chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL), mantle cell lymphoma, and a subset (~10%) of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. CD5 aberrant expression is useful in making a diagnosis of mature T-cell neoplasms. Anti-CD5 detection is diagnostic in CLL/SLL within a panel of other B-cell markers, especially one that includes anti-CD23. Anti-CD5 is also very useful in differentiating among mature small lymphoid cell malignancies. In addition, anti-CD5 can be used in distinguishing thymic carcinoma (+) from thymoma (-). Anti-CD5 does not react with granulocytes or monocytes.
There are no reviews yet.