Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>
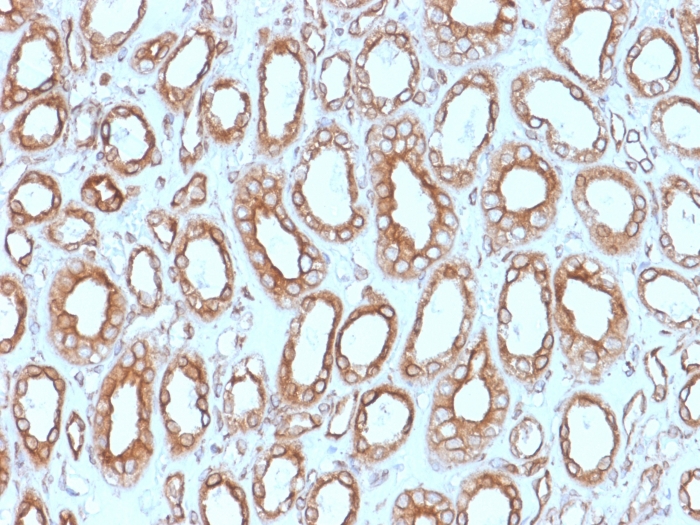
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human renal cell carcinoma stained with Calnexin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CANX/1543). HIER: Tris/EDTA, pH9.0, 45min. 2°C: HRP-polymer, 30min. DAB, 5min.
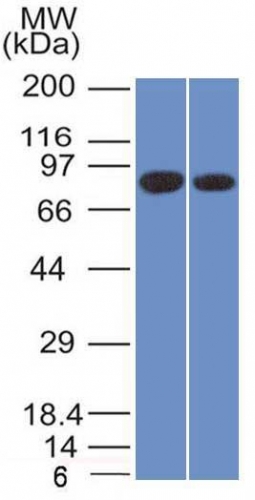
Western Blot of Analysis of PANC1 and MCF-7 cell lysates using Calnexin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CANX/1543).
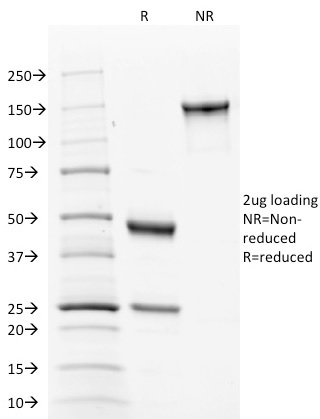
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified Calnexin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CANX/1543). Confirmation of Integrity and Purity of Antibody.
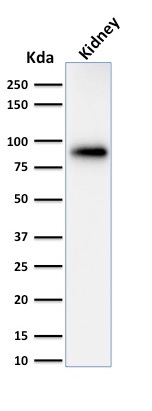
Western Blot of Analysis of human kidney tissue lysate using Calnexin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CANX/1543).
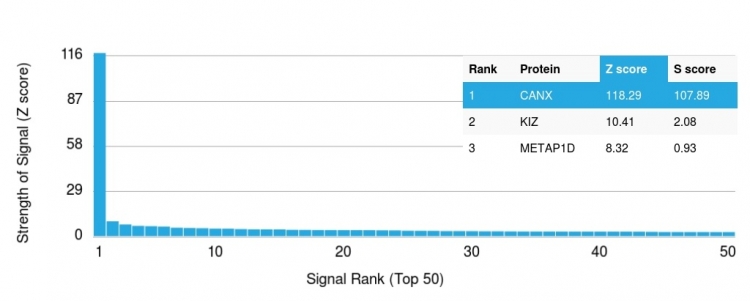
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using Calnexin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CANX/1543). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
It recognizes a protein of 90kDa, which is identified as Calnexin. Secretory and transmembrane proteins are synthesized on polysomes and translocate into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) where they are often modified by the formation of disulfide bonds, amino-linked glycosylation and folding. To help proteins fold properly, the ER contains a pool of molecular chaperones including calnexin. It is a calcium-binding, endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated protein that interacts transiently with newly synthesized N-linked glycoproteins, facilitating protein folding and assembly. It may also play a central role in the quality control of protein folding by retaining incorrectly folded protein subunits within the ER for degradation.
There are no reviews yet.