Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>
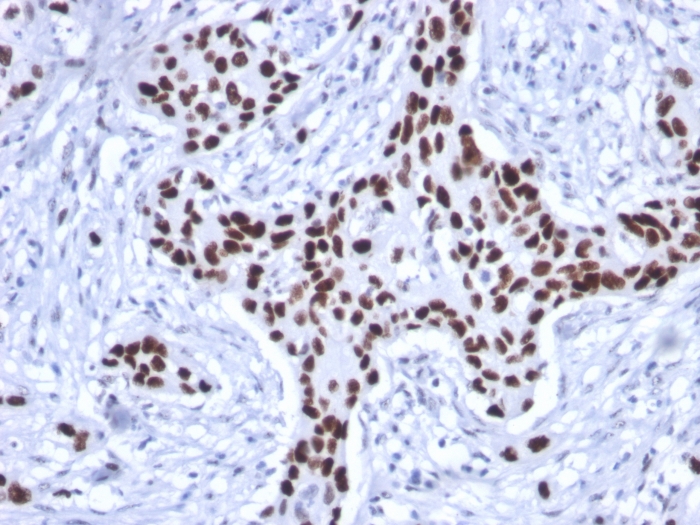
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Breast Carcinoma stained with p53 Mouse Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody (rTP53/1739)
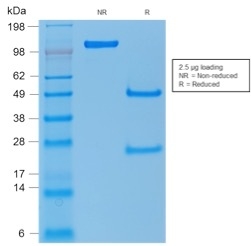
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified p53 Mouse Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody (rTP53/1739). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
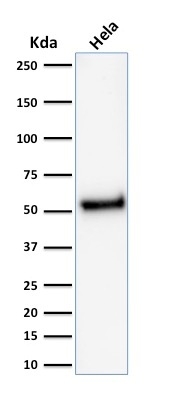
Western blot analysis of HeLa cell lysate using p53 Mouse Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody (rTP53/1739).
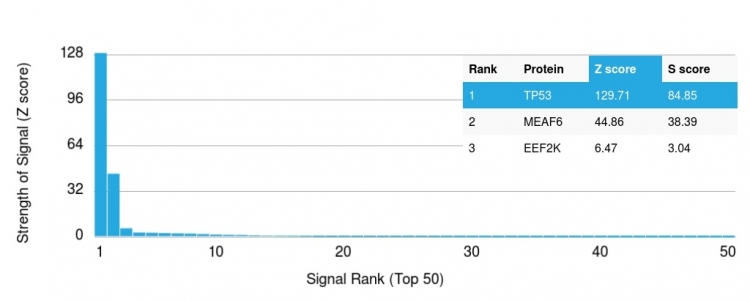
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using p53 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (rTP53/1739). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
The specificity of this monoclonal antibody to its intended target was validated by HuProtTM Array, containing more than 19,000, full-length human proteins. Recognizes a 53kDa protein, which is identified as p53 suppressor gene product. It reacts with the mutant as well as the wild form of p53. It is a tumor suppressor protein expressed in a wide variety of tissue types and is involved in regulating cell growth, replication, and apoptosis. It binds to MDM2, SV40 T antigen and human papilloma virus E6 protein. Positive nuclear staining with p53 antibody has been reported to be a negative prognostic factor in breast, lung, colorectal, and urothelial carcinoma. Anti-p53 positivity has also been used to differentiate uterine serous carcinoma from endometrioid carcinoma as well as to detect intratubular germ cell neoplasia. Mutations involving p53 are found in many malignant tumors, including breast, ovarian, bladder, colon, lung, and melanoma.
There are no reviews yet.