Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>

Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Pancreas stained with GP2 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GP2/1712).
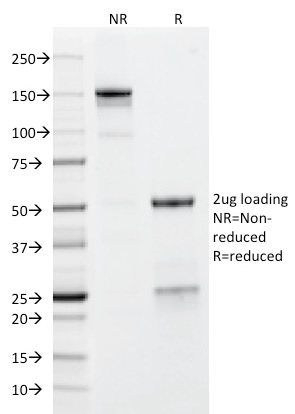
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified GP2 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GP2/1712). Confirmation of Integrity and Purity of Antibody.

Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using GP2 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (GP2/1712) Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (Monoclonal Antibody) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a Monoclonal Antibody to its intended target. A Monoclonal Antibody is considered to specific to its intended target, if the Monoclonal Antibody has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a Monoclonal Antibody binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that Monoclonal Antibody to protein X is equal to 29.
GP2 (glycoprotein 2), also known as ZAP75, is a 537 amino acid secreted protein. It is an integral membrane protein that is secreted from intracellular zymogen granules and associates with the plasma membrane via glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) linkage. GP2 is cleaved and then released into the pancreatic duct along with exocrine secretions. GP2 binds pathogens such as enterobacteria, thereby playing an important role in the innate immune response. The C-terminus of this protein is related to the C-terminus of the protein encoded by the neighboring gene, uromodulin (UMOD). GP2 is also expressed on the apical plasma membrane of specialized microfold (M) cells among enterocytes and serves as a transcytotic receptor for mucosal antigens. M cells are considered a promising target for oral vaccination against various infectious diseases.
There are no reviews yet.