Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>
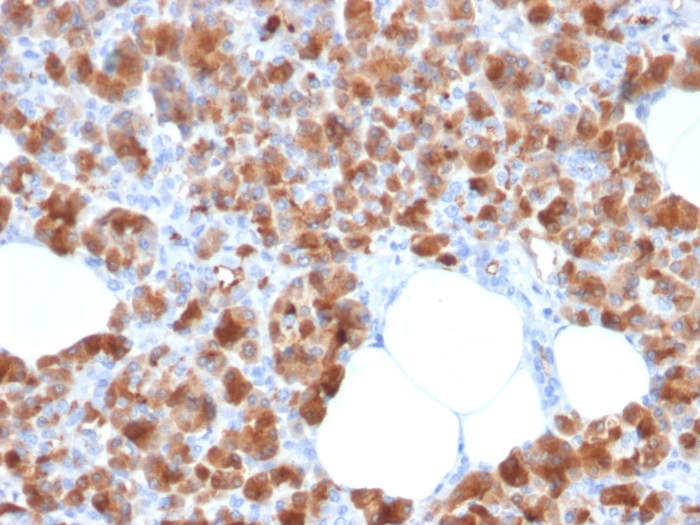
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Pancreas stained with Carboxypeptidase A1 / CPA1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPA1/2713).

SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified Carboxypeptidase A1 / CPA1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPA1/2713). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.

Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using Carboxypeptidase A1 / CPA1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPA1/2713). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (Monoclonal Antibody) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a Monoclonal Antibody to its intended target. A Monoclonal Antibody is considered to specific to its intended target, if the Monoclonal Antibody has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a Monoclonal Antibody binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that Monoclonal Antibody to protein X is equal to 29.
Human pancreatic procarboxypeptidase A exists as three different active forms, two of which are designated carboxypeptidase A1 (CPA1) and carboxypeptidase A2 (CPA2). CPA1, also known as CPA, is a 419 amino acid secreted monomeric protein that is highly expressed in pancreatic tissue. Functioning as a pancreatic exopeptidase, CPA1 uses zinc as a cofactor to catalyze the release of C-terminal amino acids from a variety of proteins, thereby playing a key role in protein digestion and degradation. Via its catalytic activity, CPA1 is also thought to be involved in zymogen (proenzyme) inhibition, probably functioning to block enzyme activation pathways. Abnormal levels of CPA1 are associated with pancreatic cancer, suggesting a possible role in either tumor progression or tumor suppression events.
There are no reviews yet.