Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>
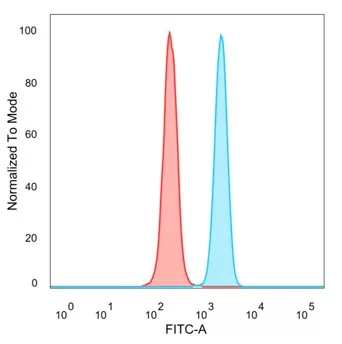
Flow Cytometric Analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. BATF3 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-BATF3-1E5) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); unstained cells (red).

SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified BATF3 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-BATF3-1E5). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
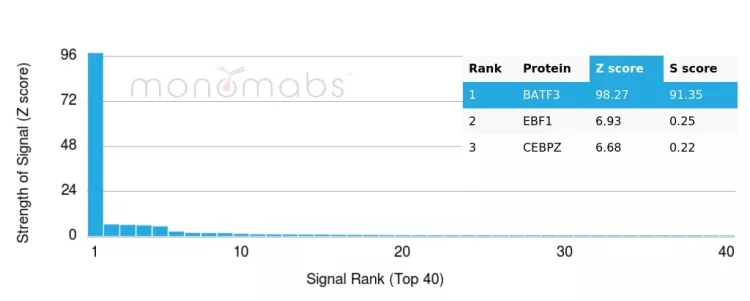
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using BATF3 Mouse Monoclonal (PCRP-BATF3-1E5). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
SNFT, also known as BATF3 (basic leucine zipper transcription factor, ATFlike 3), JUNDM1 or JDP1, is a 127 amino acid protein that localizes to the nucleus and contains one bZIP domain. Interacting with c-Jun, SNFT functions as a negative regulator of AP-1-mediated transcription, specifically by heterodimerizing with c-Jun and binding to DNA response elements. The gene encoding SNFT maps to human chromosome 1, which spans 260 million base pairs, contains over 3,000 genes and comprises nearly 8% of the human genome. Chromosome 1 houses a large number of disease-associated genes, including those that are involved in familial adenomatous polyposis, Stickler syndrome, Parkinson s disease, Gaucher disease, schizophrenia and Usher syndrome. Aberrations in chromosome 1 are found in a variety of cancers, including head and neck cancer, malignant melanoma and multiple myeloma.
There are no reviews yet.