Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>

Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human tonsil stained with SPARC / Osteonectin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (OSTN/3933). Inset: PBS instead of primary antibody; secondary only negative control.

Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human placenta stained with SPARC / Osteonectin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (OSTN/3933). HIER: Tris/EDTA, pH9.0, 45min. 2°C: HRP-polymer, 30min. DAB, 5min.
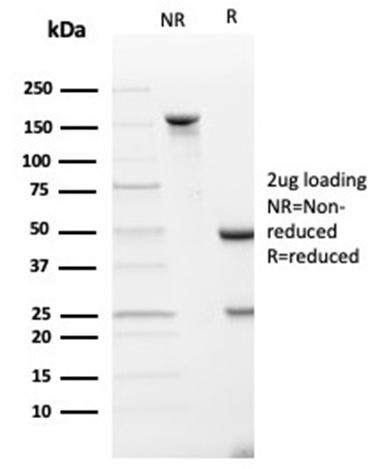
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified SPARC / Osteonectin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (OSTN/3933). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
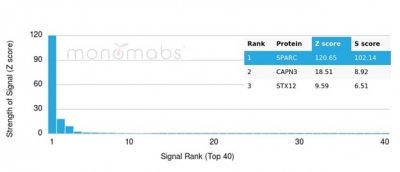
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using SPARC / Osteonectin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (OSTN/3933). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
SPARC (for secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine) is a phosphorylated, acidic, glycine-rich glycoprotein that is secreted by endothelial cells and is present in large amounts in the parietal endoderm of mouse embryos and in human placenta. It is identical to osteonectin, a protein important to bone calcification that is highly conserved between species. SPARC, which can be selectively expressed by the endothelium in response to certain types of injury, induces rounding in adherent endothelial cells in vitro. It regulates endothelial barrier function through F-Actin-dependent changes in cell shape, coincident with the appearance of intercellular gaps, which provide a paracellular pathway for extravasation of macromolecules.
There are no reviews yet.