Free Shipping in the U.S. for orders over $1000. Shop Now>>
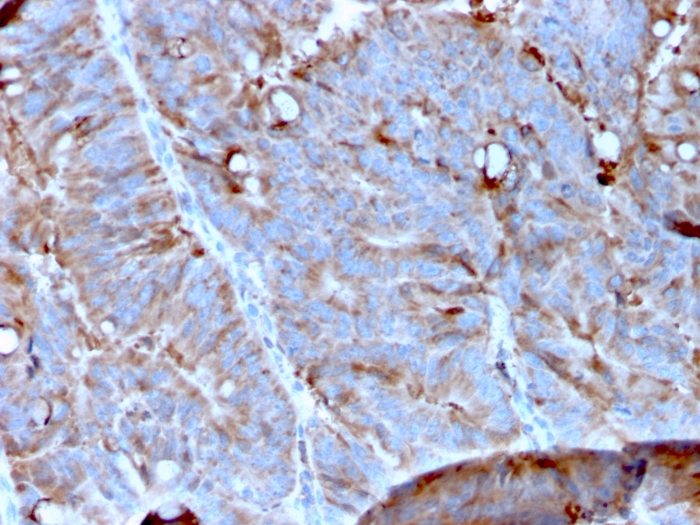
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Colon Carcinoma stained with MerTK Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (MERTK/3023).

Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Colon Carcinoma stained with MerTK Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (MERTK/3023).
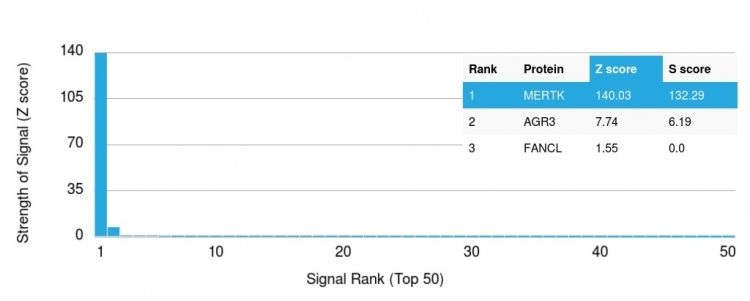
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using MerTK Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (MERTK/3023). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
MerTK, also called c-Mer, is a member of the Mer/Axl/Tyro3 receptor kinase family. It is a 984 residue transmembrane protein made up of one tyrosine kinase domain, two Fibronectin type-III domains and two immunoglobulinlike C2-type domains. MerTK is the mammalian ortholog of the chicken retroviral oncogene product v-Eyk. This protein plays a critical role in macrophage activation, platelet aggregation, clot stability and the efficient removal of apoptotic cells. Specifically, MerTK acts as a signaling molecule, triggering outer segment ingestion in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) phagocytic process. Evidence suggests that MerTK signals via interaction with phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C 纬2 (PI-PLC 纬2). When the gene encoding for MerTK is mutated, the RPE phagocytosis pathway is disrupted and autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa (RP) may result, leading to degeneration of retinal photoreceptor cells.
There are no reviews yet.