Free Shipping in the U.S. for orders over $1000. Shop Now>>
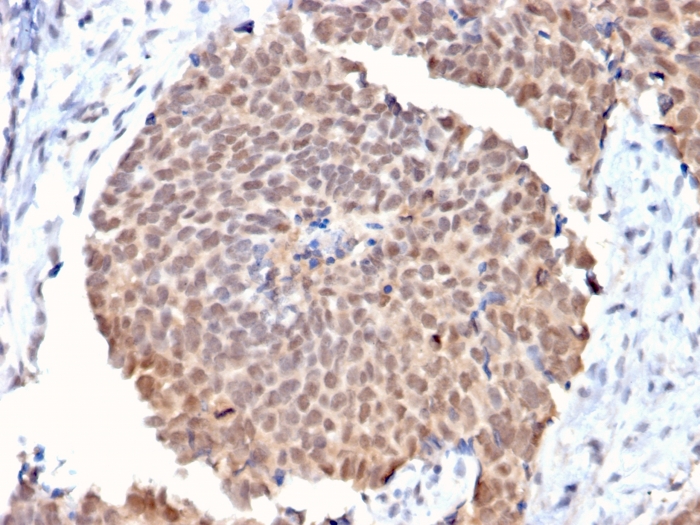
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Breast Cancer stained with FAF1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-FAF1-2).
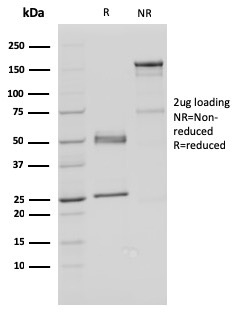
SDS-PAGE Analysis Purified FAF1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-FAF1-2). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.

Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Colon Carcinoma stained with FAF1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-FAF1-2).
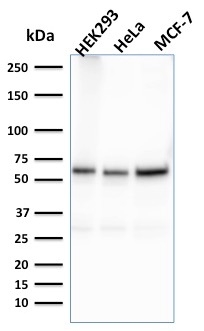
Western Blot Analysis of HEK293, HeLa, MCF-7 cell lysates using Purified FAF1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-FAF1-2).
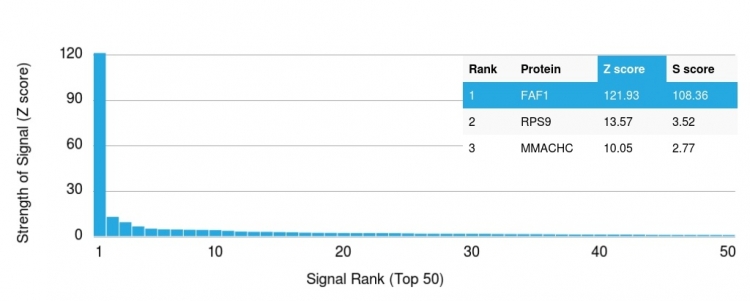
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using Fas (TNFRSF6) associated factor 1 Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-FAF1-2). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
In contrast to growth factors which promote cell proliferation, FAS ligand (FAS-L) and the tumor necrosis factors (TNFs) rapidly induce apoptosis. Cellular response to FAS-L and TNF is mediated by structurally related receptors containing a conserved 'death domain' and belonging to the TNF receptor superfamily. TRADD, FADD and RIP are FAS/TNF-RI interacting proteins that contain a death domain homologous region (DDH). TRADD (TNF-RI-associated death domain) and FADD (FAS-associated death domain) associate with the death domains of both FAS and TNF-RI via their DDH regions, while RIP associates exclusively with FAS. An additional FAS interacting protein designated FAF1, for FAS-associated protein factor-1, binds with the cytoplasmic tail of wildtype but not LPR mutant FAS. When overexpressed in cells, FAF1 enhances the efficiency of FAS-mediated apoptosis. In contrast to TRADD, FADD and RIP, FAF1 lacks a DDH and cannot induce apoptosis independently of FAS activation.
There are no reviews yet.