Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>
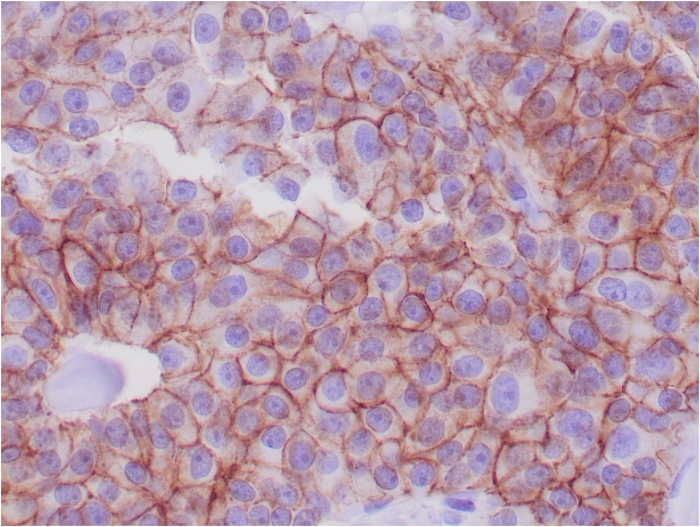
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human breast adenocarcinoma stained with E-Cadherin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CDH1/1525).
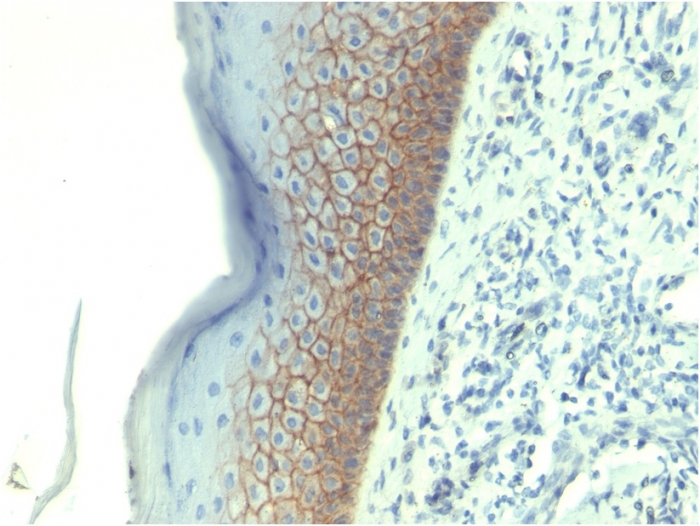
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human skin stained with E-Cadherin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CDH1/1525).
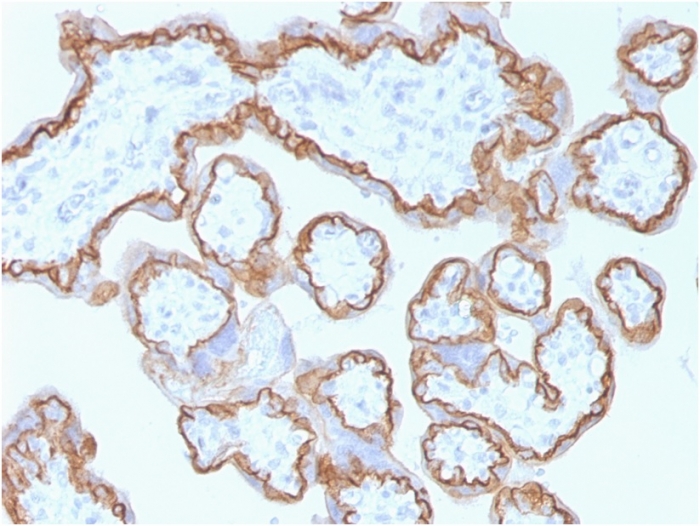
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human placenta stained with E-Cadherin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CDH1/1525).
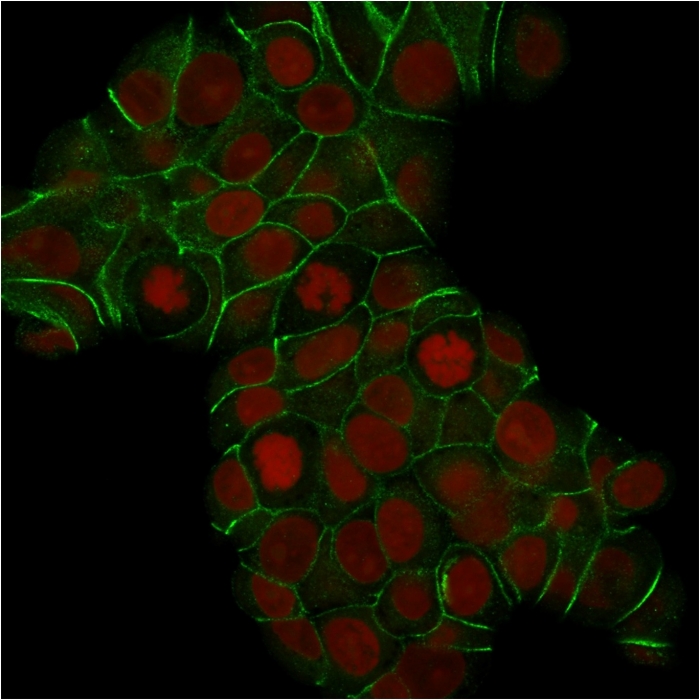
Confocal immunofluorescence analysis of MCF-7 cells. E-Cadherin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CDH1/1525) labeled with CF488 (green); nuclei labeled with RedDot.

Western blot analysis of (A) recombinant protein (B) human stomach lysates. E-Cadherin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CDH1/1525).
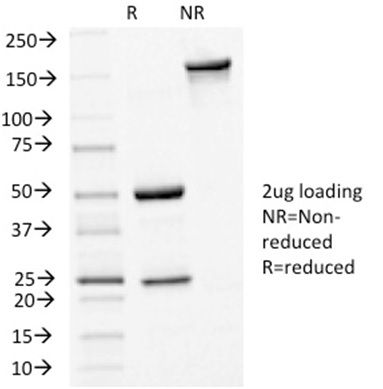
SDS-PAGE Analysis Purified E-Cadherin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CDH1/1525). Confirmation of Integrity and Purity of Antibody.
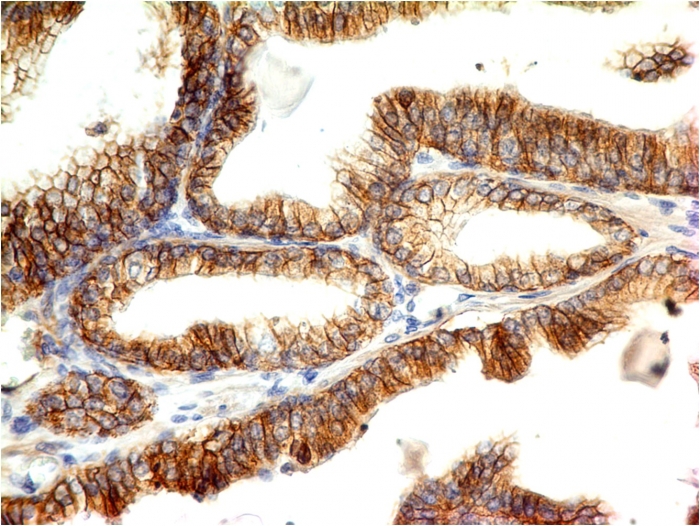
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded colon carcinoma stained with E-Cadherin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CDH1/1525).
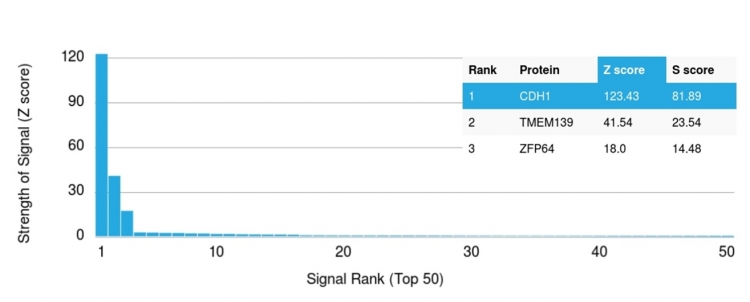
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using E-Cadherin (CDH1) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CDH1/1525). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
Recognizes a protein of 120-80kDa, identified as E-cadherin. Cadherins comprise a family of Ca2+-dependent adhesion molecules that function to mediate cell-cell binding critical to the maintenance of tissue structure and morphogenesis. The classical cadherins, E-, N- andP-cadherin, consist of large extracellular domains characterized by a series of five homologous NH2 terminal repeats. The relatively short intracellular domains interact with a variety of cytoplasmic proteins, such as 尾-catenin, to regulate cadherin function.E-cadherin plays an important role in epithelial cell adhesion. A decreased expression of E-cadherin is associated with metastatic potential and poor prognosis in breast cancer, prostate and esophageal cancer. In combination with p120 Catenin, it is useful for the differentiation between ductal (E-cadherin +) and lobular (E-cadherin -) breast carcinomas. It may also help in diagnosis of mesothelioma.
There are no reviews yet.