Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>
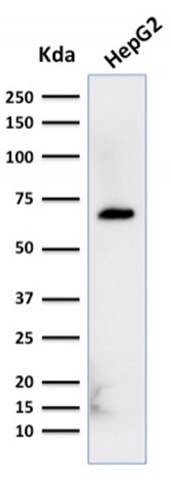
Western Blot Analysis of HepG2 cell lysate using Albumin Monospecific Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (ALB/2356).
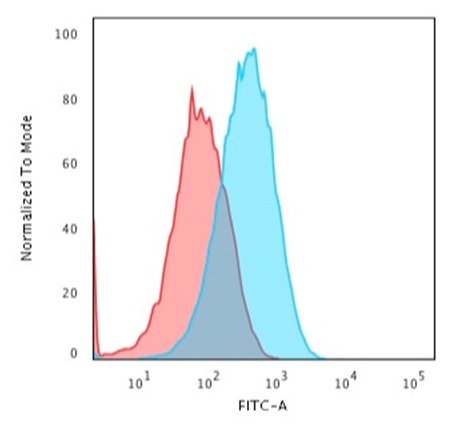
Flow Cytometric Analysis of paraformaldehyde-fixed HepG2 cells using Albumin Monospecific Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (ALB/2356) followed by goat anti-Mouse IgG-CF488 (Blue); Isotype Control (Red).
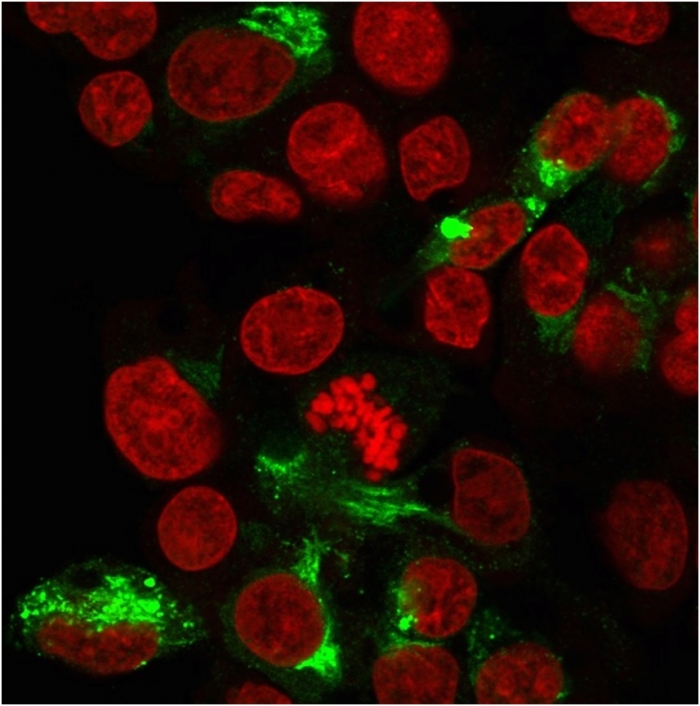
Immunofluorescent staining of paraformaldehyde-fixed HepG2 cells with Albumin Monospecific Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (ALB/2356)followed by goat anti-Mouse IgG-CF488 (Green). Nuclei are labelled with Reddot (Red).

SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified Albumin Monospecific Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (ALB/2356). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
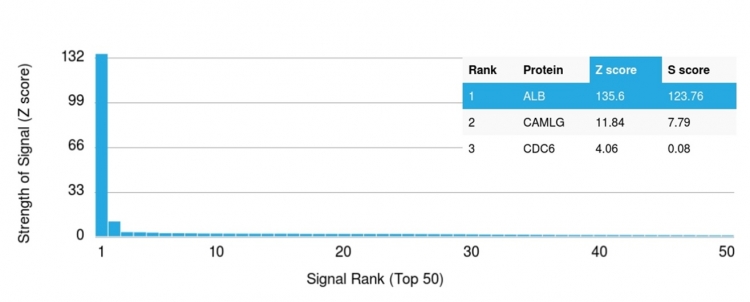
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using Albumin Monospecific Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (ALB/2356). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD’s) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD’s) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
This MAb is Monospecific to albumin and shows no significant cross-reaction with other human proteins. Albumin is a soluble, monomeric protein, which comprises about one half of the blood serum protein. Albumin functions primarily as a carrier protein for steroids, fatty acids, and thyroid hormones and plays a role in stabilizing extracellular fluid volume.Albumin is synthesized in the liver as preproalbumin, which has an N-terminal peptide that is removed before the nascent protein is released from the rough endoplasmic reticulum. The product, proalbumin, is in turn cleaved in the Golgi vesicles to produce the secreted form of albumin.
There are no reviews yet.