Free Shipping in the U.S. for orders over $1000. Shop Now>>

Flow Cytometric Analysis of PFA-fixed MCF-7 cells. SIRT2 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-SIRT2-1A8) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); unstained cells (red).

Immunofluorescence Analysis of PFA-fixed U-87 cells using SIRT2 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-SIRT2-1A8) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (green). CF640A phalloidin (red).
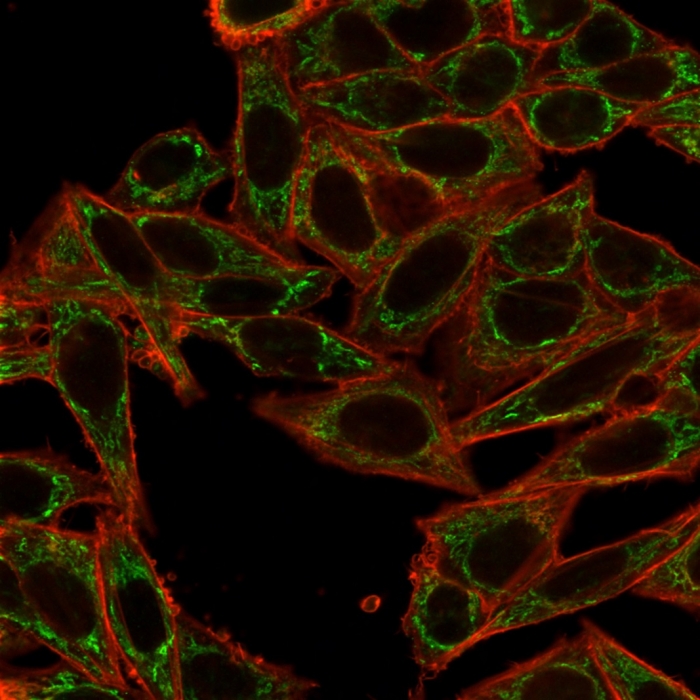
Immunofluorescence Analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells using SIRT2 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-SIRT2-1A8) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (green). CF640A phalloidin (red).

Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using SIRT2 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-SIRT2-1A8). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
The silent information regulator (SIR2) family of genes are highly conserved from prokaryotes to eukaryotes and are involved in diverse processes, including transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression, DNA-damage repair and aging. In S. cerevisiae, Sir2p deacetylates histones in a NAD-dependent manner, which regulates silencing at the telomeric, rDNA and silent mating-type loci. Sir2p is the founding member of a large family, designated sirtuins, which contain a conserved catalytic domain. The human homologs, which include SIRT1-7, are divided into four main branches: SIRT1-3 are class I, SIRT4 is class II, SIRT5 is class III and SIRT6-7 are class IV. SIRT proteins may function via mono-ADP-ribosylation of proteins. SIRT2 contains a 323 amino acid catalytic core domain with a NAD-binding domain and a large groove which is the likely site of catalysis.
There are no reviews yet.