Free Shipping in the U.S. for orders over $1000. Shop Now>>

Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human tonsil stained with HLA-Pan Rabbit Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody (HLA-Pan/2967R).
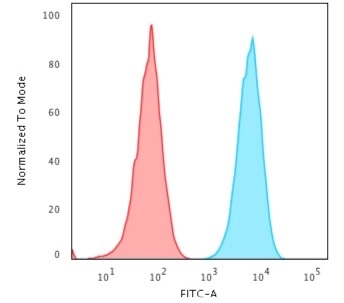
Flow Cytometric Analysis of PFA-fixed Raji cells. HLA-Pan Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (HLA-Pan/2967R) followed by goat anti-rabbit IgG-CF488 (blue); Isotype control (red).

Immunofluorescence staining of PFA-fixed Ramos cells. HLA-Pan Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (HLA-Pan/2967R) followed by goat anti-rabbit IgG-CF488 (green). Nuclei stained with RedDot.

Immunofluorescence staining of PFA-fixed Raji cells. HLA-Pan Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (HLA-Pan/2967R) followed by goat anti-rabbit IgG-CF488 (green). Nuclei stained with RedDot.
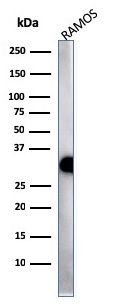
Western Blot Analysis of Ramos cell lysate using HLA-Pan Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (HLA-Pan/2967R).
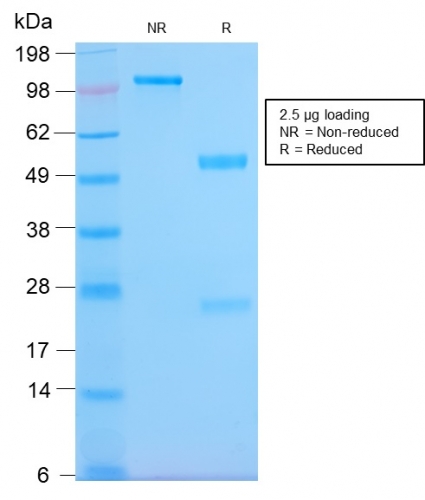

SDS-PAGE Analysis Purified HLA-Pan Rabbit Recombinant Monoclonal (HLA-Pan/2967R). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
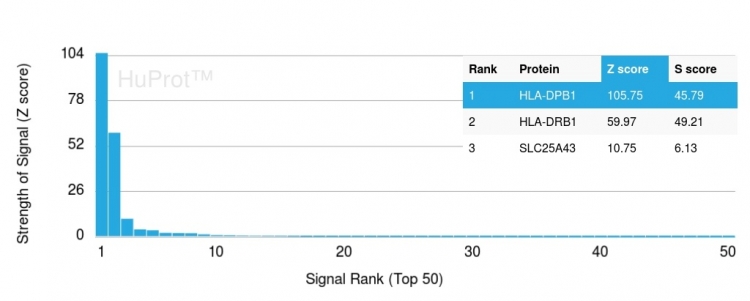
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using HLA-Pan Rabbit Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody (HLA-Pan/2967R). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
Reacts with a common epitope of human major histocompatibility (MHC) class II antigens, HLA-DP, -DQ and -DR. Human MHC class II antigens are transmembrane glycoproteins composed of an chain (36kDa) and a � � chain (27kDa). They are expressed primarily on antigen presenting cells such as B lymphocytes, monocytes, macrophages, and thymic epithelial cells and are also present on activated T lymphocytes. Human MHC class II genes are located in the HLA-D region that encodes at least six and ten � � chain genes. Three loci, DR, DQ and DP, encode the major expressed products of the human class II region. The human MHC class II molecules bind intracellularly processed peptides and present them to T-helper cells. They, therefore, have a critical role in the initiation of the immune response. It has been shown that some autoimmune diseases are associated with certain class II alleles.
There are no reviews yet.