Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>
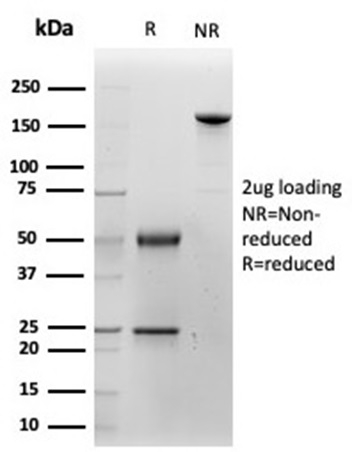
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified Cytokeratin 14 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (KRT14/4128). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.

Western blot analysis of A431 cell lysate using Cytokeratin 14 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (KRT14/4128).
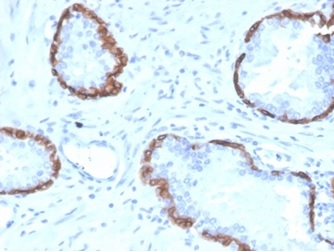
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human prostate stained with Cytokeratin 14 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (KRT14/4128). HIER: Tris/EDTA, pH9.0, 45min. 2°C: HRP-polymer, 30min. DAB, 5min.
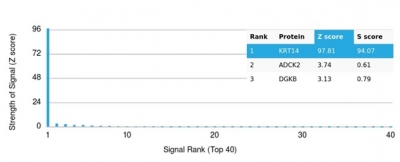
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using Cytokeratin 14 (KRT14)-Monospecific Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (KRT14/4128). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
Cytokeratin 14 is a member of the type I keratin family of intermediate filament proteins. It always pairs with the type II keratin K5 and form the primary keratin pair of the keratinocytes of stratified squamous epithelia, including the epidermis as well as mucosal non-keratinizing stratified squamous epithelia. Cytokeratin 14 is strongly expressed in the undifferentiated basal cell layer containing the stem cells and are down-regulated in the differentiating suprabasal cell layers. Otherwise, in the widely well stratified follicular outer root sheath, cytokeratin 14 is uniformly expressed throughout all layers. The expression spectrum of cytokeratin 14 in tumors corresponds well to the patterns in normal epithelia. Thus, most squamous cell carcinomas as well as malignant mesotheliomas strongly express this keratin whereas little, focal, or no expression is found in adenocarcinomas. Cytokeratin 14 may be a useful marker in the differential diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma from other epithelial tumors. Recent studies also indicate that CK14 expression in breast cancer corresponded with poor clinical outcome and that CK14 may have diagnostic value in the sub-classification of NSCLC.
There are no reviews yet.