Free Shipping in the U.S. for orders over $1000. Shop Now>>
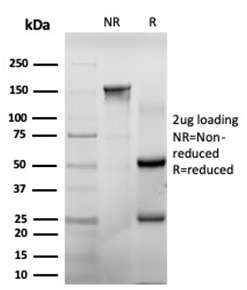
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified CHEK2 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-CHEK2-1A4). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
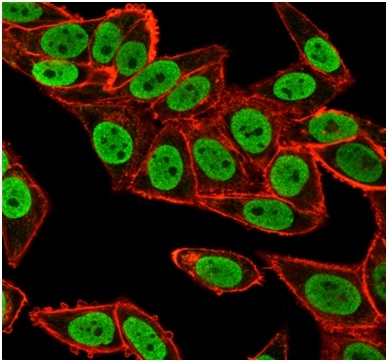
Immunofluorescence analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. CHEK2 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-CHEK2-1A4) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (green). Microtubules stained with phalloidin.

Immunofluorescence analysis of PFA-fixed K562 cells. CHEK2 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-CHEK2-1A4) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (green). Phalloidin (red).
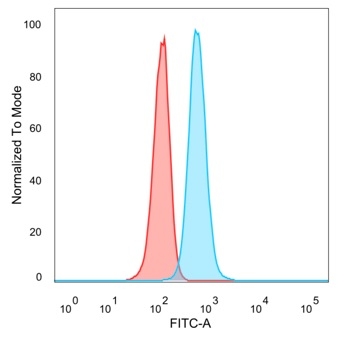
Flow cytometric analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. CHEK2 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-CHEK2-1A4) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue), unstained cells (red).
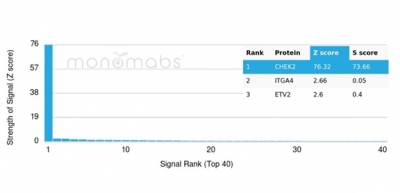
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using CHEK2 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-CHEK2-1A4). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
Recognizes a serine/threonine protein kinase that is a required check-point to mediate cell cycle arrest, activation of DNA repair and apoptosis.In response to DNA damage and replication blocks, cell cycle progression is halted through the control of critical cell cycle regulators. The protein encoded by this gene is a cell cycle checkpoint regulator and putative tumor suppressor. It contains a forkhead-associated protein interaction domain essential for activation in response to DNA damage and is rapidly phosphorylated in response to replication blocks and DNA damage. When activated, the encoded protein is known to inhibit CDC25C phosphatase, preventing entry into mitosis, and has been shown to stabilize the tumor suppressor protein p53, leading to cell cycle arrest in G1. Also, this protein interacts with and phosphorylates BRCA1, allowing BRCA1 to restore survival after DNA damage. Mutations in this gene have been linked with Li-Fraumeni syndrome, a highly penetrant familial cancer phenotype usually associated with inherited mutations in TP53. Mutations in this gene are thought to confer a predisposition to sarcomas, breast cancer, and brain tumors.
There are no reviews yet.