Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>

Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Spleen stained with CD79a Mouse Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody (rIGA/764).
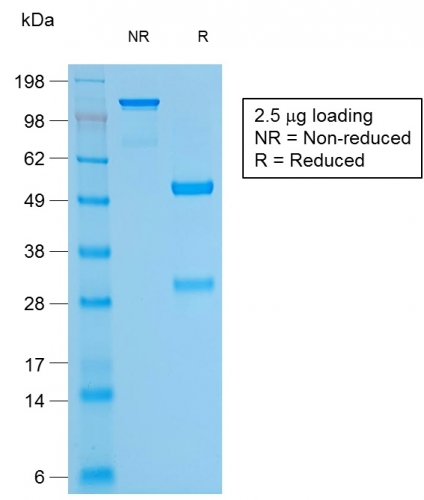
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified CD79a Mouse Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody (rIGA/764). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
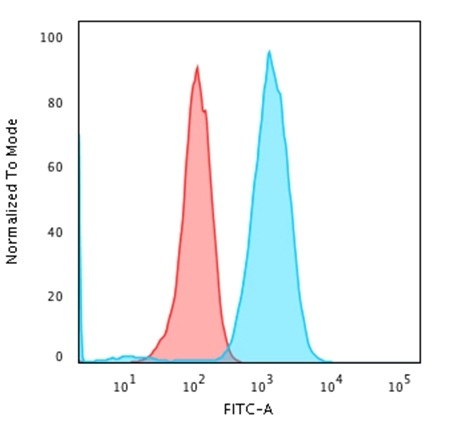
Flow Cytometric Analysis of Raji cells using CD79a Mouse Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody (rIGA/764) followed by Goat anti-Mouse IgG-CF488 (Blue); Isotype Control (Red).
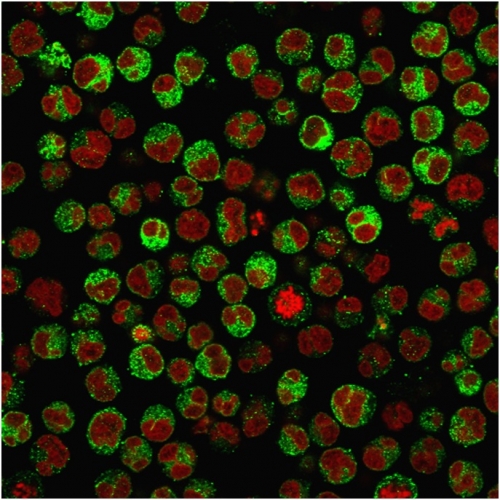
Immunofluorescence Analysis of PFA-fixed Raji cells labeling CD79a with CD79a Mouse Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody (rIGA/764) followed by Goat anti-Mouse IgG-CF488 (Green). The nuclear counterstain is Reddot (Red)

Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using CD79a Mouse Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody (rIGA/764). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
A disulphide-linked heterodimer, consisting of mb-1 (or CD79a) and B29 (or CD79b) polypeptides, is non-covalently associated with membrane-bound immunoglobulins on B cells. This complex of mb-1 and B29 polypeptides and immunoglobulin constitute the B cell Ag receptor. CD79a first appears at pre B cell stage, early in maturation, and persists until the plasma cell stage where it is found as an intracellular component. CD79a is found in the majority of acute leukemias of precursor B cell type, in B cell lines, B cell lymphomas, and in some myelomas. It is not present in myeloid or T cell lines. Anti-CD79a is generally used to complement anti-CD20 especially for mature B-cell lymphomas after treatment with Rituximab (anti-CD20). This antibody will stain many of the same lymphomas as anti-CD20, but also is more likely to stain B-lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia than is anti-CD20. Anti-CD79a also stains more cases of plasma cell myeloma and occasionally some types of endothelial cells as well.
There are no reviews yet.