Free Shipping in the U.S. for orders over $1000. Shop Now>>
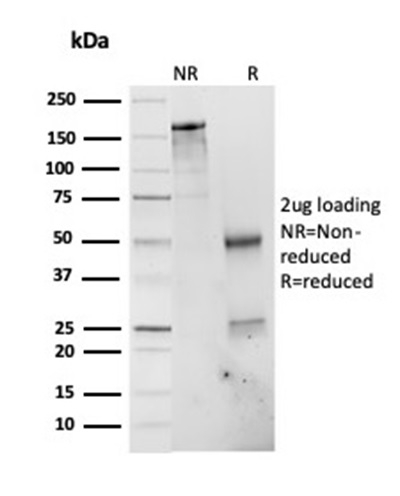
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified PSMD4Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-PSMD4-3). Confirmation of Integrity and Purity of Antibody.
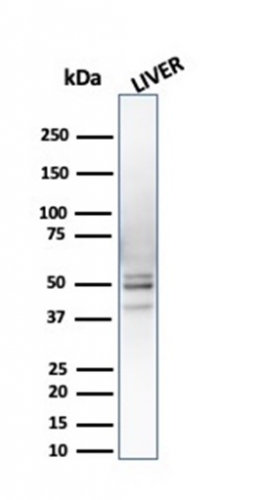
Western Blot Analysis of Liver tissue lysate using PSMD4Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-PSMD4-3).
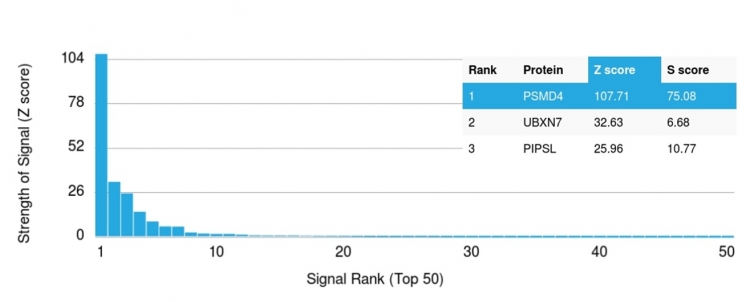
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 4 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-PSMD4-3). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
In eukaryotic cells, selective breakdown of cellular proteins is ensured by two distinct pathways. First, appropriate proteins are tagged for degradation by ubiquitination. Second, these multiubiquitinated proteins are degraded by the highly selective 26S Proteasome protein-destroying machinery. At specific stages of development, embryo- and tissue-specific components of the 26S Proteasome are formed, which are termed Rpn10a through Rpn10e, or alternatively pUb-R2 through pUb-R5. All members of this family can be generated by a single Rpn10 gene by developmentally regulated alternative splicing. The pUb-R2 subunit, originally identified as S5a (also designated antisecretory factor and multiubiquitin chain binding protein) is ubiquitously expressed and may perform proteolysis constitutively in a wide variety of cells. pUb-R4 and pUb-R5 may have embryo- or tissue-specific expression and may play specialized roles in early embryonic development.
There are no reviews yet.