Free Shipping in the U.S. for orders over $1000. Shop Now>>
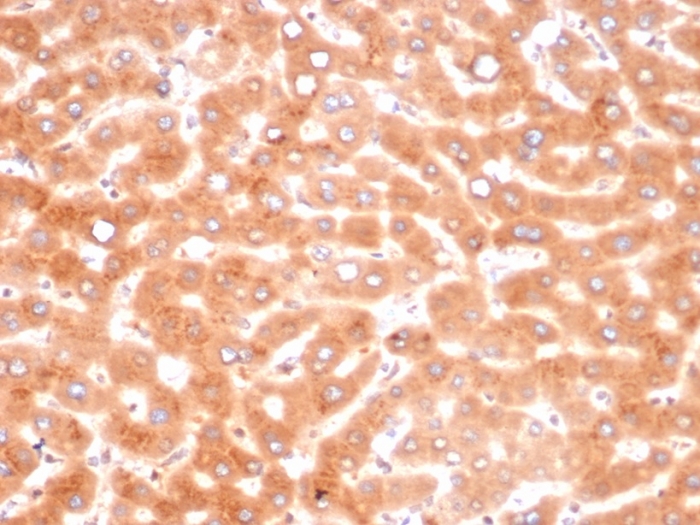
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human liver stained with Alpha-1-Antichymotrypsin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (SERPINA3/4187).
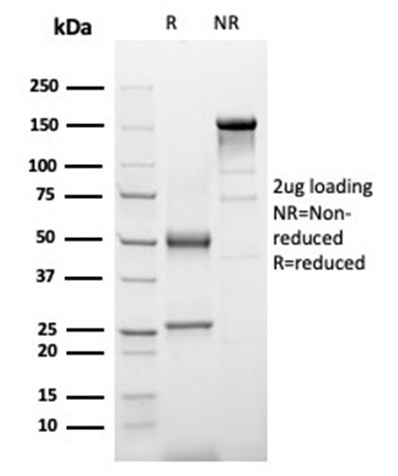
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified AACT Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (SERPINA3/4187). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
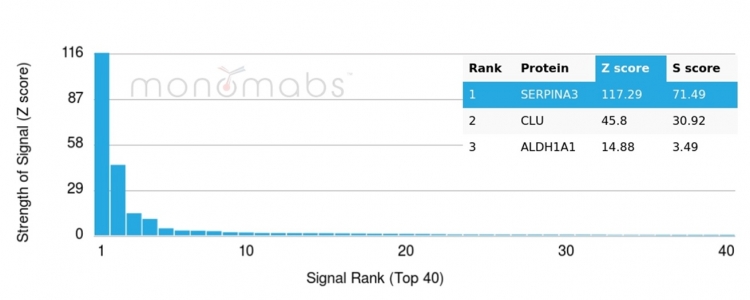
Analysis of Protein Array containing >19,000 full-length human proteins using Monospecific to Alpha-1-Antichymotrypsin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (SERPINA3/4187). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
It recognizes a protein of 65-76kDa, which is identified antichymotrypsin (AACT). AACT is a plasma protease inhibitor synthesized in the liver as a single glycopeptide chain. In human, the normal serum level of AACT is about one-tenth that of 伪 1-antitrypsin (AAT), with which it shares nucleic acid and protein sequence homology. Both are major acute phase reactants; their concentrations in plasma increase in response to trauma, surgery and infection. Elevated levels of AACT are widely, but not universally, reported in the cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of AD patients. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and its SDS-stable complex with AACT are in widespread use as markers for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. AACT deficiency may also be a possible cause of chronic liver disease. AACT antibody reacts with histiocytes and histiocytic neoplasms. It is widely used to identify histiocytes and tumors derived from them. Acinar tumors of the pancreas and salivary gland may also exhibit AACT positivity.
There are no reviews yet.