Learn about our comprehensive antibody validation methods to ensure monospecificity. Antibody Validation>>
24 December, 2023 by Anshul (neobio)

Ever struggled with unpredictable results in your research due to poorly specified antibodies? Understanding and ensuring the validation of antibody specificity can alleviate this common issue and significantly enhance the accuracy of your investigations. Antibodies are essentially the detectives of the immune system, identifying and neutralizing foreign objects like bacteria and viruses. The key to their ability to recognize the right target lies in their specificity, a unique aspect determined by the polypeptide loops in their variable domains.
Antibody specificity refers to the ability of an antibody to discriminate between antigenic variants. This characteristic, determined by unique polypeptide loops in the antibody’s variable domains, is what allows the immune response to hone in on the exact antigen of interest, providing valuable insights into our understanding of an array of diseases and conditions. However, it’s not enough to have highly specific antibodies; it’s equally crucial to confirm their specificity through careful validation.
When we continually lean on advanced biotechnologies for critical research, the validation of antibody specificity is no longer an option but an absolute necessity. As a researcher, ensuring this validation allows you to rule out the interference of non-specific binding, yielding reliable and repeatable results for your investigations.
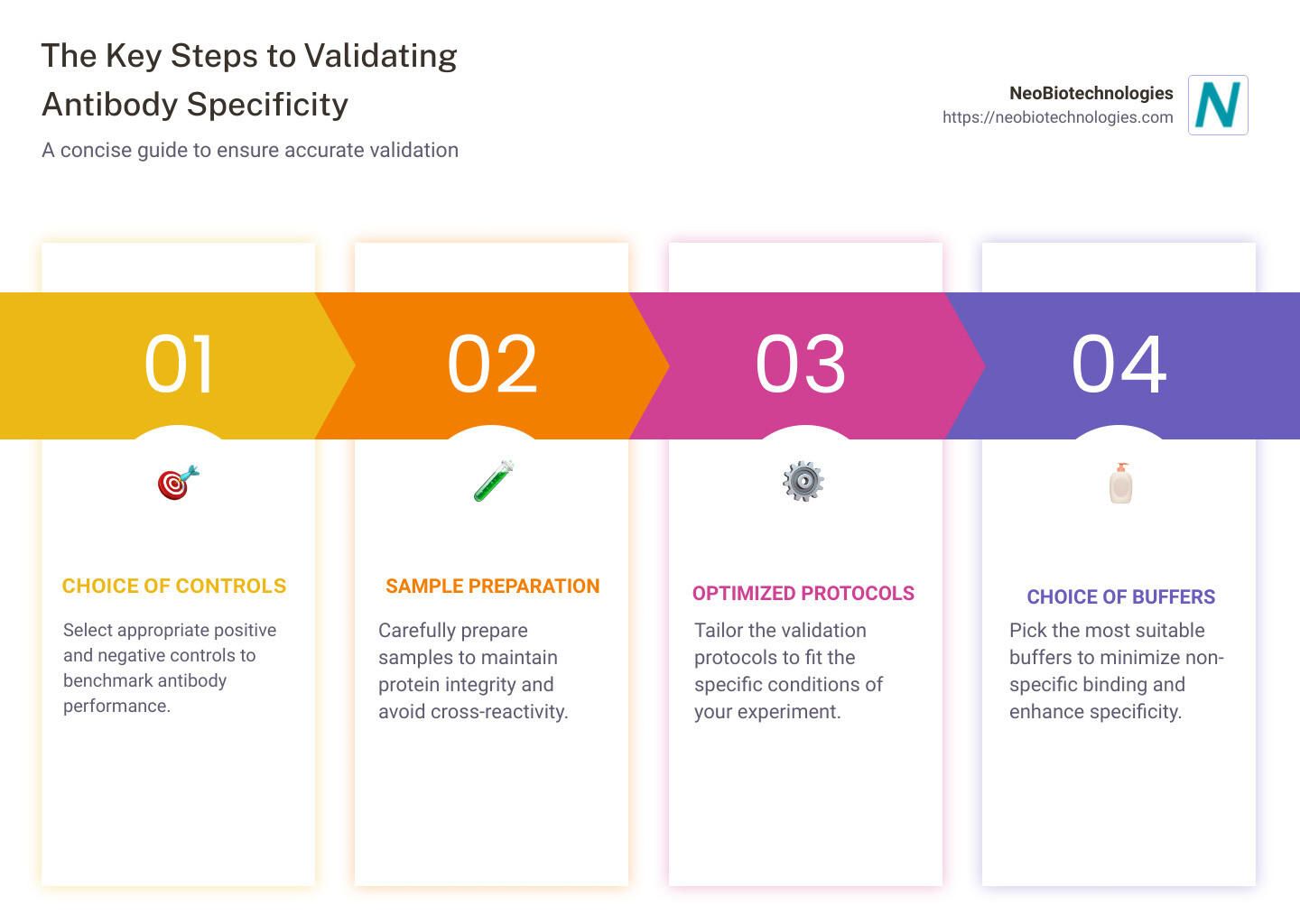
A few indicators to keep in mind while validating your antibodies’ specificity include the use of positive and negative controls, correct preparation of your samples, optimized incubation durations, and the appropriate choice of buffers.
In a nutshell, here’s what you’ll need to consider:
If you’ve been feeling lost in your quest to validate your antibodies, these key points will guide you through the process.
As we delve into the importance and process of validating antibody specificity, we’ll explore the five pillars of antibody validation, practical approaches, and the commitment of leading biotech companies like NeoBiotechnologies, dedicated to providing highly validated, monospecific Rabbit Recombinant Monoclonal Antibodies, suitable for varied applications including Immunohistochemistry, Flow Cytometry, Western Blotting, and Immunofluorescence.
By assuring specificity, we ensure our research maintains integrity.
The validation of antibody specificity is a multifaceted process. To ensure the specificity and reproducibility of an antibody, scientists around the world have agreed upon five key strategies, often referred to as the ‘five pillars’ of antibody validation. These pillars offer a comprehensive approach to verifying an antibody’s specificity, and when used in conjunction, they can provide a high level of confidence in the antibody’s performance.
The first pillar of validation involves genetic strategies, which compare binding signals in cells expressing the target protein to control cells where the target gene has been knocked out by methods like CRISPR or RNA interference (RNAi). If an antibody is specific, it should show no binding activity when the target protein is absent. Although creating reliable knock-out cell lines can be laborious, the availability of ready-made KO cell lines, such as those offered by NeoBiotechnologies, can accelerate assay development and enhance the viability of this strategy.
The second pillar, orthogonal strategies, involves comparing the abundance of a target protein using an antibody-independent assay (like transcriptomics or targeted proteomics) with results obtained using antibodies across a range of relevant samples. This method, although potentially challenging due to the non-linear and often highly variable relationship between mRNA and protein abundance, can provide additional validation of antibody specificity.
The third pillar involves the use of independent antibody strategies. This involves immunoprecipitating the target with one antibody and subsequently detecting it by western blotting with another antibody against the same target. This provides confidence that both antibodies are binding to the correct protein, reinforcing the specificity of the antibodies.
The fourth pillar concerns the expression of tagged proteins. In this method, an epitope tag is added to the target protein. The antibody’s reaction to this tagged protein can provide additional evidence towards its specificity. This method is particularly useful when studying post-translational modifications.
The fifth and final pillar involves the use of immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry. This powerful technique combines the specificity of immunoprecipitation with the accurate protein identification capabilities of mass spectrometry. This combination provides a robust and comprehensive method for validating antibody specificity.
In conclusion, these five pillars offer a robust framework for the validation of antibody specificity. By implementing each of these strategies, researchers can have a high degree of confidence in the specificity of their antibodies, ensuring reproducible and reliable results. Dr. Atul K. Tandon, founder and CEO of NeoBiotechnologies, emphasizes the importance of these strategies in ensuring the quality and reliability of their Antibodies, thereby supporting the scientific community in their various applications.
To ensure the specificity and reliability of an antibody, several practical approaches can be employed. These include binary and ranged testing, recombinant strategies, complementary strategies, and careful consideration of validation protocols.
Binary and ranged strategies are fundamental in the validation of antibody specificity. In binary testing, antibodies are tested in a binary fashion – positive or negative – to confirm their ability to bind to their target. This strategy is a critical first step in validation and can be performed using endogenous or heterologous models expressing the target of interest.
Ranged testing, on the other hand, involves testing the antibody across a range of expression levels of the target. This approach is crucial in understanding the optimal working conditions of an antibody, as it allows researchers to observe the antibody’s behavior in various biological contexts where the expression of the target is high or low in one cell line or tissue relative to another.
When the protein of interest is expressed at low levels, a recombinant strategy is often employed for antibody validation. This involves the use of recombinant proteins or heterologous expression in a surrogate cell line.
Recombinant strategy offers several advantages, such as the ability to verify the cross-reactivity of an antibody with protein isoforms or conserved family members. It can also test the sensitivity of an antibody through titration of the target protein by expression or dilution. For instance, NeoBiotechnologies manufactures over 1,000 highly validated, monospecific Rabbit Recombinant Monoclonal Antibodies, ideal for various applications like Immunohistochemistry, Flow Cytometry, and Western Blotting.
Complementary strategies provide additional information regarding antibody specificity or functionality. These approaches can include the use of peptide arrays and/or ELISAs to determine the specificity of an antibody for a post-translational modification (PTM), and various peptide blocking methods to prevent antibody binding to a defined antigen.
Functional assays, such as neutralization or protein activation using an antibody as an agonist, are also included in complementary strategies. These methods provide additional data to support results generated using the other validation strategies.
The choice and preparation of positive and negative controls, the selection of appropriate buffers, and the optimization of protocols are vital factors in the validation of antibody specificity. Different antibodies may require different conditions and protocols for optimal functionality and specificity.
For instance, the incubation period for each antibody needs to be determined as it can vary dramatically from a minimum of one hour to overnight at 4°C. Other factors, such as working dilutions, blocking conditions, and the use of native vs denatured conditions, also need to be optimized.
In conclusion, the validation of antibody specificity is a multi-faceted process that requires careful consideration of various factors. By leveraging a combination of these practical strategies, researchers can ensure the reliability and reproducibility of their results, further advancing their scientific endeavors.
Rigorous validation of antibody specificity is a crucial step in research as it ensures the reliability and reproducibility of results. Validation processes such as verifying specificity through knockdown/knockout of target expression, optimizing antibody dilutions, repeating the experimental results, and confirming the observed effect with a complementary method, all contribute to the precision of the research outcome.
The reproducibility of research antibodies remains a high priority in the scientific community. Although a universal framework of standards has not yet emerged, there is general agreement that rigorous validation should include, at a minimum, evaluation of antibody specificity and reproducibility .
NeoBiotechnologies is at the forefront of providing highly validated and specific monoclonal antibodies for various applications. They manufacture over 1,000 highly validated, monospecific Rabbit Recombinant Monoclonal Antibodies, ideal for Immunohistochemistry, Flow Cytometry, Western Blotting, or Immunofluorescence .
Each antibody is subjected to rigorous testing and validation processes to ensure their specificity, selectivity, and reproducibility. NeoBiotechnologies takes pride in their commitment to deliver reliable and high-quality antibodies to the scientific community, ensuring that researchers can trust the products they use in their important work.
For more information on antibody validation and how NeoBiotechnologies can support your research, visit their resources on antibody validation. You can also explore their wide range of monospecific Rabbit Recombinant Monoclonal Antibodies and learn more about their validation processes.