Free Shipping in the U.S. for orders over $1000. Shop Now>>

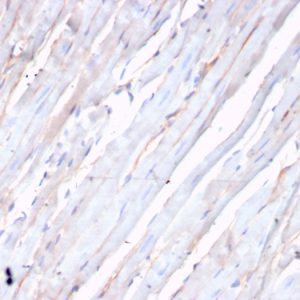
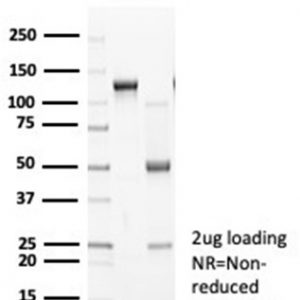
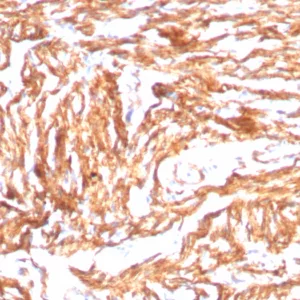
The N-cadherin protein, also known as Cadherin-2 or CD325, is encoded by the CDH2 gene, which is located on chromosome 18q11.2. With a molecular weight of approximately 130 kDa, N-cadherin is a transmembrane protein primarily found at adherens junctions, where it mediates calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion. It undergoes post-translational modifications, including glycosylation, phosphorylation, and proteolytic cleavage, which regulate its function and stability. N-cadherin is expressed in various tissues and organs, including the brain, heart, kidney, and skeletal muscle. It is particularly abundant in neuronal tissues, playing a crucial role in synaptic plasticity and neuronal development. Additionally, N-Cadherin is expressed in mesenchymal tissues and is involved in tissue morphogenesis during embryonic development.
Functionally, N-cadherin mediates homophilic cell–cell adhesion, facilitating tissue organization, cell migration, and signaling processes. Dysregulation of N-cadherin expression or function has been implicated in various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and cardiovascular diseases. In cancer, increased N-cadherin expression is associated with tumor invasion, metastasis, and poor prognosis in several malignancies. As such, N-Cadherin has emerged as a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment.
Multiple monoclonal antibodies have been studied for their effectiveness in blocking N-cadherin-mediated tumor migration and invasion. One such antibody, called GC-4, binds to the EC1 domain of N-cadherin molecules, disrupting their ability to adhere and thus impeding tumor cell movement. GC-4 has demonstrated inhibition of Akt signaling, a pathway involved in cancer progression, and has shown effectiveness in suppressing migration and invasion of various cancer cell types, including melanoma, bladder, ovarian, and breast cancer cells in experimental setups. Moreover, in vivo experiments have indicated that pretreatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells with GC-4 can hinder homing these cells to the bone marrow. This result suggests that GC-4 might be beneficial in limiting the spread of tumor cells in melanoma, multiple myeloma (MM), and AML by impeding their movement through endothelial barriers and their colonization in the bone marrow. Additionally, GC-4 has shown potential in enhancing the sensitivity of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells to imatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, by blocking N-cadherin engagement between CML cells and stromal cells. Furthermore, other monoclonal antibodies, such as 1H7 and 2A9, targeting different regions of N-cadherin have demonstrated efficacy in reducing tumor growth and inhibiting muscle invasion and lymph node metastasis in a prostate cancer mouse model. These findings highlight the therapeutic potential of monoclonal antibodies against N-cadherin in combating cancer progression and metastasis.
NeoBiotechnologies offers a variety of antibodies against N-cadherin that have been validated for ELISA, flow cytometry, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting [https://www.neobiotechnologies.com/shop/?s=n-cadherin].
Cadherin-2, CDw325, Neural cadherin, Cadherin-2 N cadherin neuronal; Cadherin-2 type 1; Cadherin-2; Calcium dependent adhesion protein neuronal; CD325; CDH2; CDHN; CDw325; N-Cadherin; NCAD
Cardiovascular, Developmental Biology, Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation
Showing all 4 results

Showing all 4 results