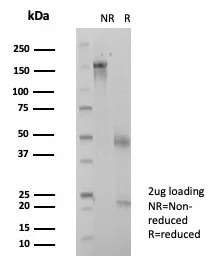
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified ZSCAN12 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-ZSCAN12-2B2). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.

Flow cytometric analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. ZSCAN12 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-ZSCAN12-2B2) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue), unstained cells (red).
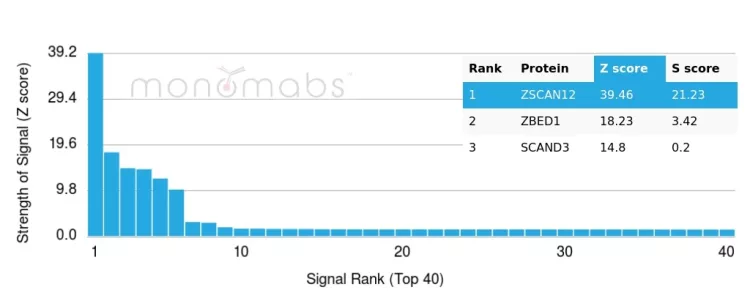
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using ZSCAN12 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-ZSCAN12-2B2). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
Zinc-finger proteins contain DNA-binding domains and have a wide variety of functions, most of which encompass some form of transcriptional activation or repression. The majority of zinc-finger proteins contain a Kruppel-type DNA binding domain and a KRAB domain, which is thought to interact with KAP1, thereby recruiting histone modifying proteins. Belonging to the Kruppel C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family, ZFP96 (zinc finger protein 96 homolog), also known as ZSCAN12 (zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing protein 12) and zinc finger protein 305, is a 604 amino acid nuclear protein that contains one SCAN box domain and 11 C2H2-type zinc fingers. ZFP96 is upregulated by 8-fold from day 13 of pregnancy to day 1 post-partum, suggesting that ZFP96 functions as a transcription factor by switching off pro-survival genes and/or upregulating pro-apoptotic genes of the corpus luteum.
There are no reviews yet.