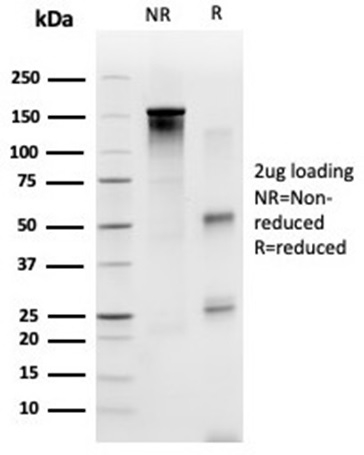
SDS-PAGE Analysis Purified SP100 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-SP100-1B9). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
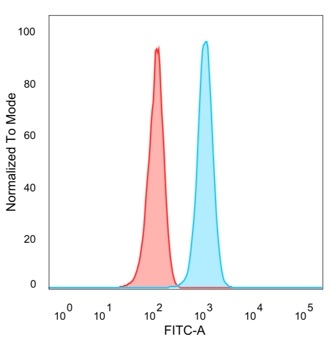
Flow cytometric analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. SP100 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-SP100-1B9) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); unstained cells (red).

Immunofluorescence Analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells stained using SP100 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-SP100-1B9) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488. Membrane stained with phalloidin.
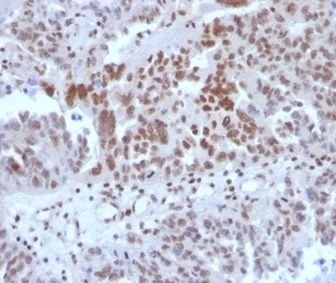
IHC analysis of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human colon. Strong nuclear staining using PCRP-SP100-1B9 at 2ug/ml in PBS for 30min RT. HIER: Tris/EDTA, pH9.0, 45min. 2 °: HRP-polymer, 30min. DAB, 5min.

IHC analysis of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human tonsil. Strong nuclear staining using PCRP-SP100-1B9 at 2ug/ml in PBS for 30min RT. HIER: Tris/EDTA, pH9.0, 45min. 2 °: HRP-polymer, 30min. DAB, 5min.
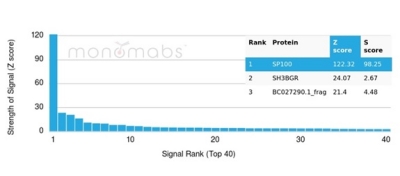
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using SP100 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-SP100-1B9). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
The human SP100 gene encodes an autoantigen that co-localizes with PML and NDP52 in distinct nuclear domains, called nuclear dots (NDs) or ND10 nuclear bodies. Papova-, adeno-, and herpesviruses begin their transcription and DNA-replication at NDs, which play a role in autoimmunity, viral infections and in the etiology of acute promyelocytic leukemia. SP-100 is an interferon inducible protein that has two splice variants. One splice variant contains a highly conserved copy of the DNA-binding high mobility group 1 protein sequence, and thus represents a novel HMG-box protein. This alternatively spliced variant of SP-100 has a unique expression and localization pattern that is distinct from the SP-100 full-length protein. The SP100 protein is covalently modified by the small ubiquitin-related protein SUMO-1. SP-100 contains a functional nuclear localization signal and an ND-targeting region, which overlaps with the SP-100 homodimerization domain.
There are no reviews yet.