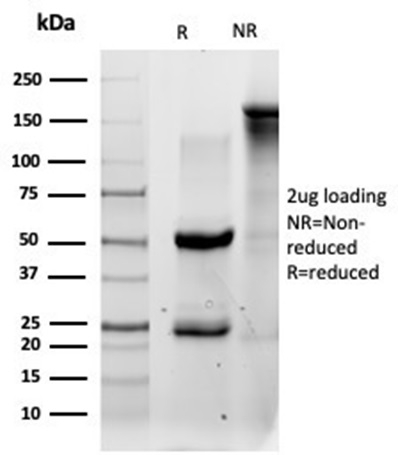
SDS-PAGE Analysis Purified QKI Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-QKI-2F10) Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
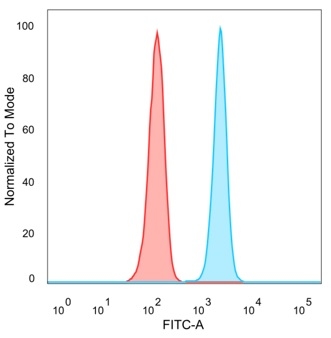
Flow cytometric analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. QKI Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-QKI-2F10) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); isotype control (red).
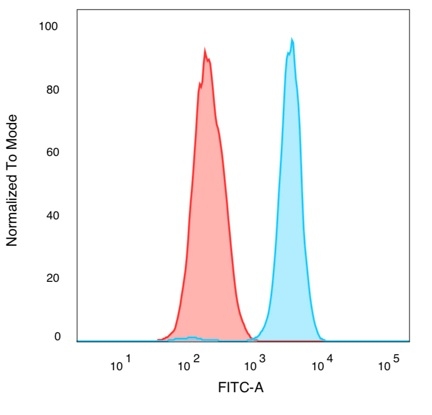
Flow cytometric analysis of PFA-fixed K562 cells. QKI Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-QKI-2F10) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); isotype control (red).
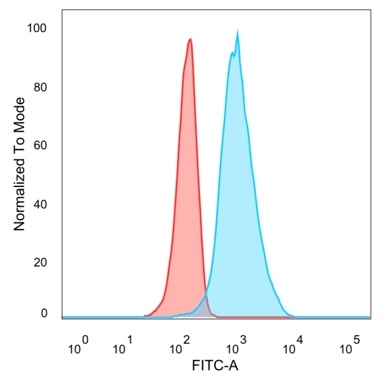
Flow cytometric analysis of PFA-fixed U87 cells. QKI Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-QKI-2F10) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); isotype control (red).
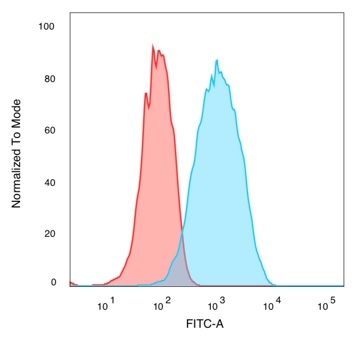
Flow cytometric analysis of PFA-fixed MCF7 cells. QKI Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-QKI-2F10) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); isotype control (red).
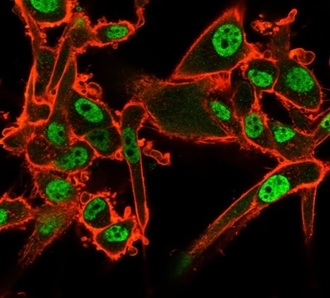
Immunofluorescence Analysis of PFA-fixed U87 cells. Staining localized to the nucleoplasm using QKI Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-QKI-2F10) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (green). CF640R phalloidin (red).
QKI, also known as HKQ, QK, QK3 or quaking, is a 341 amino acid protein that localizes to both the cytoplasm and the nucleus and contains one KH domain. Expressed in the frontal cortex of the brain, QKI functions as an RNA-binding protein that plays an important role in myelinization and specifically binds to the RNA core sequence 5'-NACUAAY-N(1,20)-UAAY-3'. Additionally, QKI regulates pre-mRNA splicing, and mRNA export and is involved in protecting and promoting the stability of select mRNAs. QKI may be methylated by PRMT1 and may also be phosphorylated at its C-terminus, an event that decreases QKI mRNA-binding affinity. Defects or deletions in the gene encoding QKI are associated with astrocytic tumors and may be involved in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Multiple isoforms of QKI exist due to alternative splicing events.
There are no reviews yet.