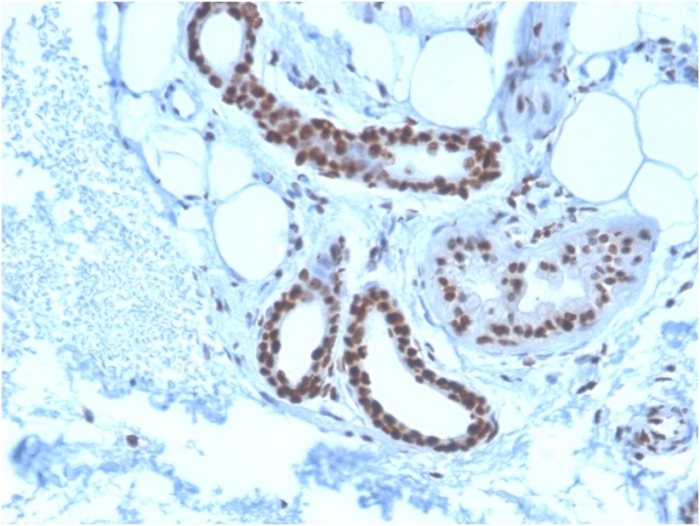
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Basal Cell Carcinoma stained with Nucleophosmin-Monospecific Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (NPM1/3285).
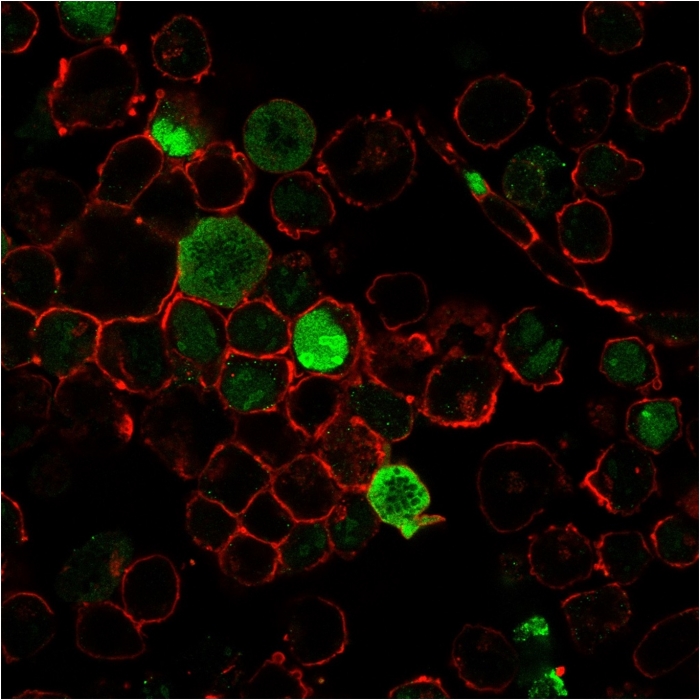
Immunofluorescence staining of K562 cells using Nucleophosmin-Monospecific Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (NPM1/3285) followed by goat anti-Mouse IgG conjugated to CF488 (green). Nuclei are stained with Reddot.

Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using Nucleophosmin-Monospecific Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (NPM1/3285) Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (Monoclonal Antibody) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD’s) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD’s) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a Monoclonal Antibody to its intended target. A Monoclonal Antibody is considered to specific to its intended target, if the Monoclonal Antibody has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a Monoclonal Antibody binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that Monoclonal Antibody to protein X is equal to 29.
Recognizes a 33kDa glycoprotein, identified as Nucleophosmin (NPM). It is predominantly localized in the nucleus of cells in most tissues. NPM is involved in ribosomal assembly and rRNA transport. It is an abundant protein that is highly phosphorylated by Cdc2 kinase during mitosis. This phosphoprotein moves between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. It is thought to be involved in several processes including regulation of the ARF/p53 pathway. A number of genes are fusion partners, in particular the anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene on chromosome 2. Mutations in exon 12 affecting the C-terminus of the protein are associated with an aberrant cytoplasmic location. Mutations in this gene are associated with acute myeloid leukemia. The antibody may be a useful aid for classification of acute myeloid leukemia.
There are no reviews yet.