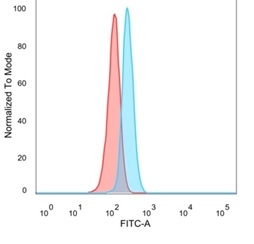
Flow cytometric analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. NFIA Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-NFIA-2C6) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); isotype control (red).
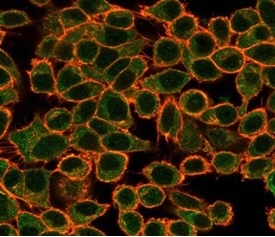
Immunofluorescence Analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells stained using NFIA Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-NFIA-2C6) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (green). CF640A phalloidin (red).
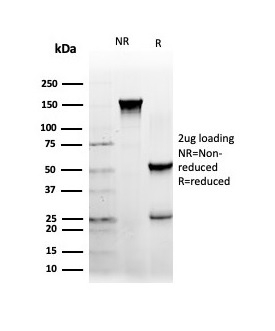
SDS-PAGE Analysis Purified NFIA Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-NFIA-2C6). Confirmation of Integrity and Purity of Antibody.
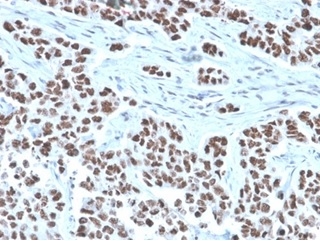
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human lung stained with NFIA Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-NFIA-2C6). HIER: Tris/EDTA, pH9.0, 45min. 2 °: HRP-polymer, 30min. DAB, 5min.
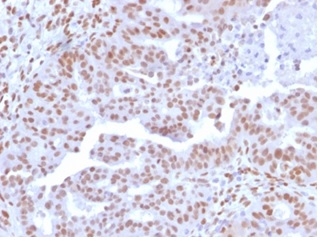
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human colon carcinoma stained with NFIA Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-NFIA-2C6). HIER: Tris/EDTA, pH9.0, 45min. 2 °: HRP-polymer, 30min. DAB, 5min.

Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using NFIA Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-NFIA-2C6). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
NF-1, also designated CTF, consists of a family of CCAAT-box-binding proteins that stimulate DNA replication and activate transcription. Analysis of human NF-1 messenger RNA has revealed two forms of the NF-1 protein arising from an alternate splicing of a single NF-1 gene. NF-1 binds its consensus DNA element as a homodimer via an amino-terminal DNA-binding domain, and activates transcription through a putatively novel, proline-rich, carboxy-terminal transactivation domain. The NF-1 protein has been shown to recognize and bind the adenovirus type 2 promoter and activate transcription of herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase genes. The NF-1 consensus element has been found in the upstream promoter region of myriad eukaryotic genes, including that of Ha-Ras, 伪-globin, HSP 70, GRP 78, Histone H1, myelin basic protein and in the Xenopus laevis vitellogenin gene promoter.
There are no reviews yet.