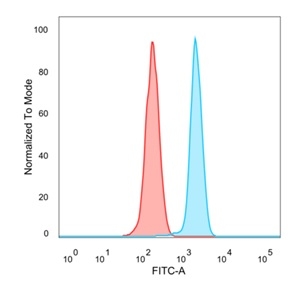
Flow Cytometric Analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. MXI1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-MXI1-1A3) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); unstained cells (red).
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified MXI1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-MXI1-1A3). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.

Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using MXI1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-MXI1-1A3). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
It is now well established that Myc regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation involves a family of related transcription factors. One such factor, Max, is an obligate heterodimeric partner for Myc and can also form heterodimers with at least four related proteins designated Mad 1, Mxi1 (also designated Mad 2), Mad 3 and Mad 4. Like Mad 1 and Mxi1, association of Mad 3 and Mad 4 with Max results in transcriptional repression. Both Myc and the Mad proteins have short half-lives and their synthesis is tightly regulated, while Max expression is constitutive and relatively stable. Two related mammalian cDNAs have been identified and shown to encode Mad- binding proteins. Both possess sequence homology with the yeast transcription repressor Sin3 including four conserved paired amphipathic helix (PAH) domains. mSin3A and mSin3B specifically interact with the Mad proteins via their second paired amphipathic helix domain (PAH2). It has been suggested that Mad-Max heterodimers repress transcription by tethering mSin3 to DNA as corepressors.
There are no reviews yet.