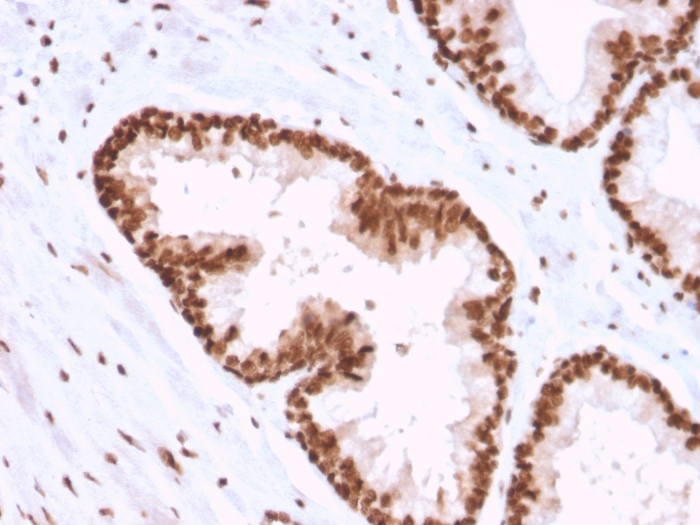
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Prostate Carcinoma stained with APEX Nuclease I Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-APEX1-2).
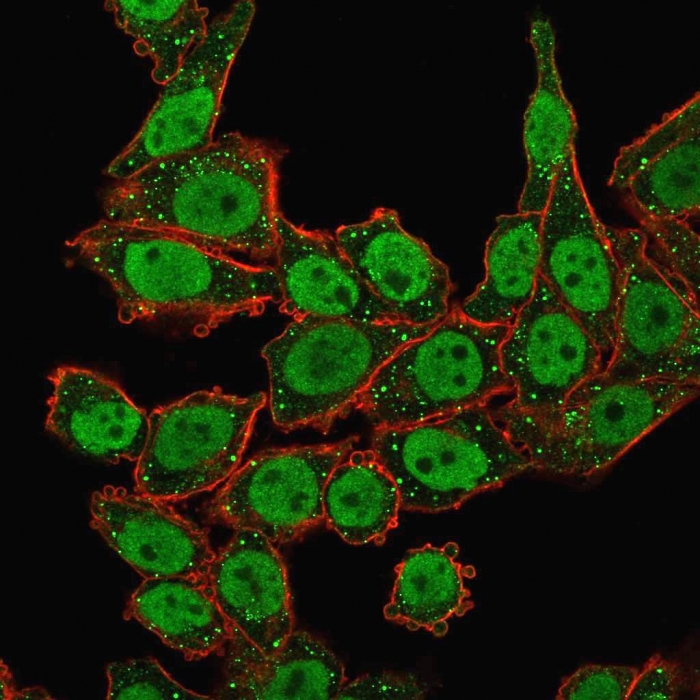
Immunofluorescence Analysis of human HeLa cells labeling APEX Nuclease I with APEX Nuclease I Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-APEX1-2) followed by Goat anti-Mouse IgG-CF488 (Green). Phalloidin CF640 stains the membrane red.
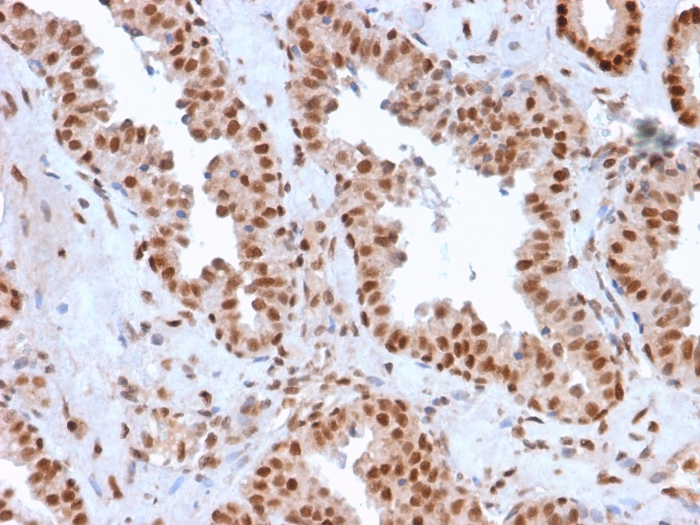
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Prostate Carcinoma stained with APEX Nuclease I Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-APEX1-2).
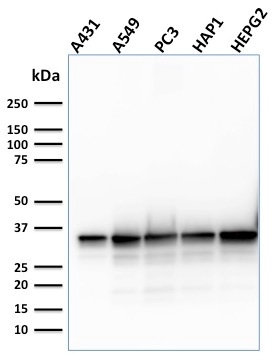
Western Blot Analysis of Human A431, A549, PC3, HAP1, HePG2, cell lysate using APEX Nuclease I Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-APEX1-2).
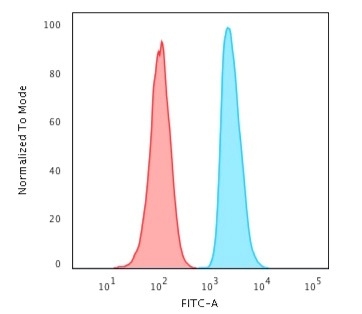
Flow Cytometric Analysis of HeLa cells using APEX Nuclease I Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-APEX1-2). Goat anti-Mouse IgG-CF488 (Blue); Isotype Control (Red).

SDS-PAGE Analysis Purified APEX Nuclease I Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-APEX1-2). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
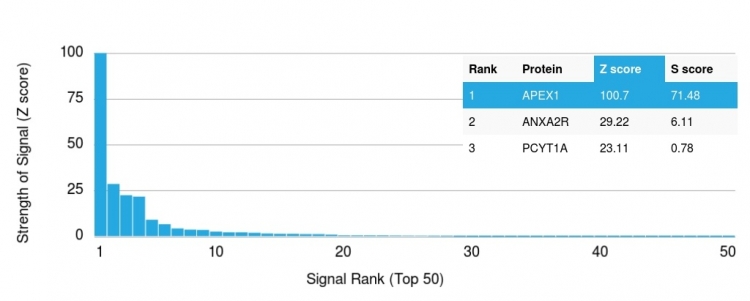
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using APEX Nuclease I Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-APEX1-2). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SDs) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SDs) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
APEX / APE1 is a multifunctional protein that plays a central role in the cellular response to oxidative stress. The two major activities of APEX1 in DNA repair and redox regulation of transcriptional factors. Functions as a apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) endodeoxyribonuclease in the DNA base excision repair (BER) pathway of DNA lesions induced by oxidative and alkylating agents. Patients with genetic variants in APEX1 and XRCC1 have been shown to have a higher risk of lung cancer. Elevated APEX1 levels observed in human testicular cancer may be related to relative resistance to therapy and therefore may serve as a diagnostic marker for refractory disease.
There are no reviews yet.