
SDS-PAGE Analysis Purified GPI Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-GPI-1). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.

Immunofluorescence Analysis of human MCF-7 cells labeling GPI with GPI Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-GPI-1) followed by Goat anti-Mouse IgG-CF488 (Green). The nuclear counterstain is Reddot (Red)

Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Breast Carcinoma stained with GPI Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-GPI-1).
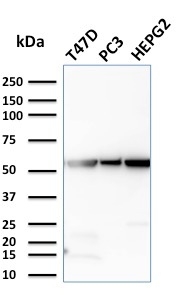
Western Blot Analysis of T47D, PC3, HePG2 cell lysates using GPI Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-GPI-1).
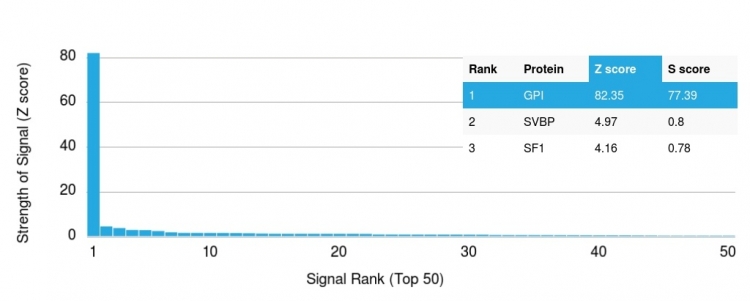
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using Glucose 6-Phosphate Isomerase Monoclonal Antibody (CPTC-GPI-1). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
Besides it’s role as a glycolytic enzyme, mammalian GPI can function as a tumor-secreted cytokine and an angiogenic factor (AMF) that stimulates endothelial cell motility. GPI is also a neurotrophic factor (Neuroleukin) for spinal and sensory neurons. Defects in GPI are the cause of hemolytic anemia non-spherocytic due to glucose phosphate isomerase deficiency.
There are no reviews yet.