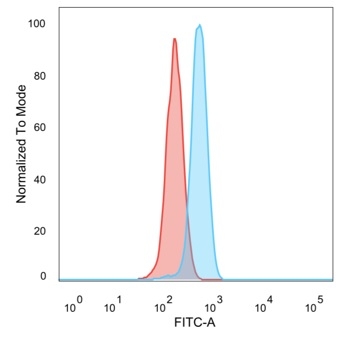
Flow Cytometric Analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. UBE3A / E6-AP Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-UBE3A-1A2) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); unstained cells (red).
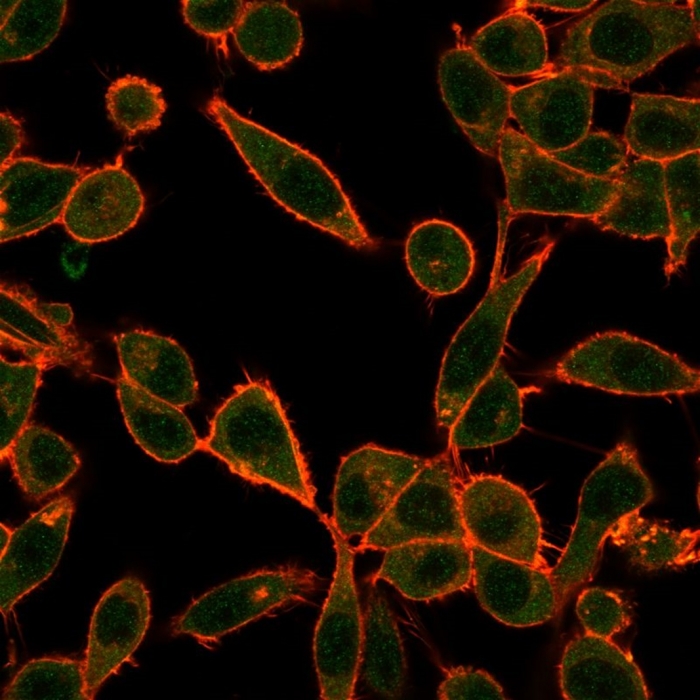
Immunofluorescent Analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. UBE3A / E6-AP Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-UBE3A-1A2) followed by IgG-CF488 (green), counterstained with phalloidin.
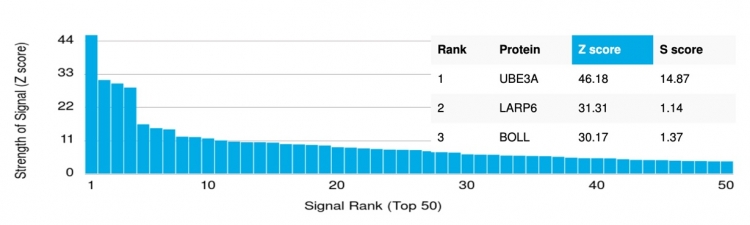
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using UBE3A / E6-AP Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-UBE3A-1A2). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
E6-associating protein (E6-AP), also designated ubiquitin protein ligase E3A(UBE3A), is a component of the ubiquitin-mediated proteolytic pathway thatselectively targets proteins for degradation by the 26S Proteasome. Ubiquitin(Ub) is directly conjugated to protein substrates by the transfer of Ub from anE2 ubiquitin conjugating enzyme to the target protein. This conjugation is facil-itated by the enzymatic activity of E3 ubiquitin ligase family members such asE6-AP. Several substrates of E6-AP have been identified and include the tumorsuppressor protein p53 and the mammalian homolog of Rad23, HHR23A.Previous studies have indicated that E6-AP associates with the humanpapillomavirus E6 oncogene, which forms a complex with p53 and therebypotentiates E6-AP mediated ubiquitination of p53. Genetic mutations thatimpair E6-AP activity result in the accumulation of p53 in the cytoplasm, andin many instances, these mutations are associated with the development ofthe rare neurodevelopmental disorder Angelman syndrome (AS), which ischaracterized by severe motor dysfunction and mental retardation.
There are no reviews yet.