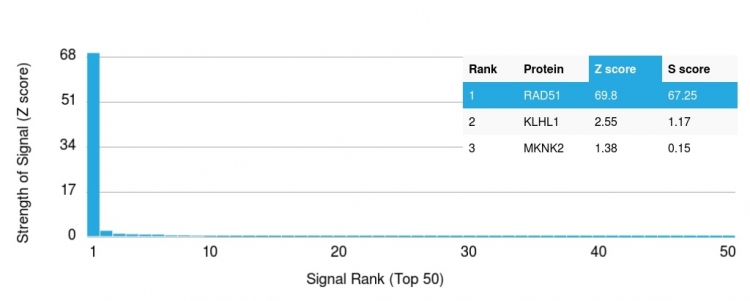
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using RAD51 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (RAD51/2765) Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (Monoclonal Antibody) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a Monoclonal Antibody to its intended target. A Monoclonal Antibody is considered to specific to its intended target, if the Monoclonal Antibody has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a Monoclonal Antibody binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that Monoclonal Antibody to protein X is equal to 29.
RAD51 is one of the key factors of DNA repair by homologous recombination and has been shown to have anti-apoptotic activity in tumor cells. RAD51 protein interacts with a variety of tumor suppressor proteins including p53, BRCA1 and BRCA2. Elevated expression of RAD51 enhances radio-resistance of human tumor cells. Overexpression of RAD51 protein in tumor cells renders them resistant against cytotoxic drugs like Cisplatin. RAD51 interacts with BRCA1 and BRCA2 to influence subcellular localization and cellular response to DNA damage. BRCA2 inactivation may be a key event leading to genomic instability and tumorigenesis from deregulation of RAD51. High-level expression of RAD51 has been observed in a variety of human malignancies.RAD51 overexpression correlates with histological grading of the tumor in invasive ductal mammary carcinoma.
There are no reviews yet.