
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human lung stained with Surfactant Protein D Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (SFTPD/4363).
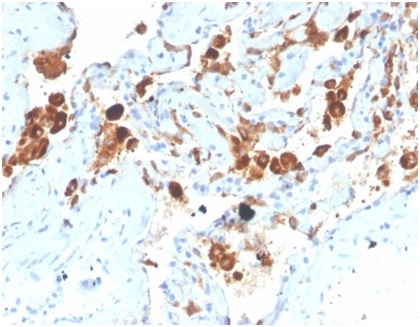
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human lung stained with Surfactant Protein D Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (SFTPD/4363).

SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified Surfactant Protein D Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (SFTPD/4363). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.

Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using Pulmonary Surfactant-Associated Protein D Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (SFTPD/4363). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
Pulmonary surfactant is primarily responsible for lowering the surface tension at the air-liquid interface in the alveoli, a process that is essential for normal respiration. Pulmonary surfactant is a mixture of phospholipids and proteins, including four distinct surfactant-associated proteins (SPs), SP-A, SP-B, SP-C, SP-D. SP-B and SP-C are predominantly hydrophobic proteins that associate with lipids to promote the absorption of surfactant phospholipids and to reduce the surface tension in the alveoli. SP-A and SP-D are large multimeric proteins belonging to the family of calcium-dependent lectins, designated Collectins, which contribute to the innate immune system. Both SP-A and SP-D have been shown to protect against microbial challenge through binding to the lipid components of the bacterial cell wall and facilitating the rapid removal of microbials.
There are no reviews yet.