
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified PBX1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-PBX1-3C8). Confirmation of Integrity and Purity of Antibody.
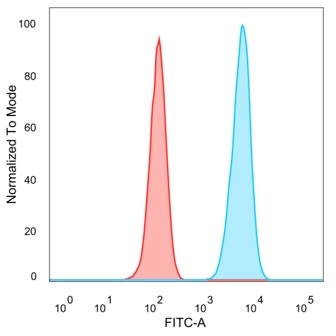
Flow cytometric analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. PBX1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-PBX1-3C8) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); isotype control (red).
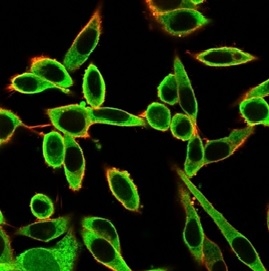
Immunofluorescence Analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells stained using PBX1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-PBX1-3C8) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (green). CF640A phalloidin (red).
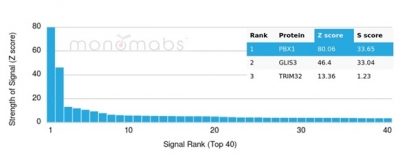
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using PBX1-Monospecific Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-PBX1-3C8). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
Pbx 1, 2, 3 and 4 are members of the TALE (three amino acid loop extension) family of homeodomain-containing proteins. Human pre-B cell acute leukemias are frequently associated with a t(1;19)(q23;p13.3) chromosomal rearrangement, which creates a chimeric gene encoding a fusion between the E2A and Pbx 1 gene products. Pbx 2 and Pbx 3 share 92% and 94% respective identities with Pbx 1 over a 266 amino acid region flanking their homeobox domains, while all three proteins are quite divergent at their amino- and carboxy-termini. Two forms of Pbx 1 and Pbx 3 each differ primarily in their carboxy-termini and result from alternative mRNA splicing. Unlike other homeotic selector genes which are expressed transiently during development and differentiation, Pbx gene transcripts are ubiquitously expressed in both fetal and adult tissues and cell lines. Additionally, Pbx 2 and Pbx 3 transcripts are detected in lymphoid cells, which do not express Pbx 1. Pbx 4 expression is confined to the testis, especially to spermatocytes in the pachytene stage of the first meiotic prophase.
There are no reviews yet.