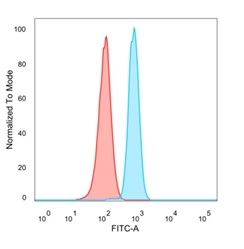
Flow Cytometric Analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. MBNL3 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-MBNL3-1D11) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); unstained cells (red).

SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified MBNL3 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-MBNL3-1D11). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.

Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using MBNL3 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-MBNL3-1D11). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
Pre-mRNA splicing is a critical step in the posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression. Several protein complexes are involved in proper mRNA splicing and transport. The muscleblind proteins, MBNL1, MBNL2 and MBNL3, promote inclusion or exclusion of specific exons on different pre-mRNAs by antagonizing the activity of CUG-BP and ETR-3-like factors bound to distinct intronic sites. MBNL1 and 2, which associate with expanded CUG repeats in vitro, localize to the nuclear foci in both DM1 and DM2 (myotonic dystrophy types 1 and 2), suggesting that the nuclear accumulation of mutant RNA is pathogenic in DM1, therefore implicating MBNL1 and 2 in the pathogenesis of both disorders. MBNL3, a 354 amino acid protein, inhibits expression of muscle differentiation, opposite to the function of MBNL1, which functions as a promoter of muscle differentiation. MBNL3 shows strong expression in placenta.
There are no reviews yet.