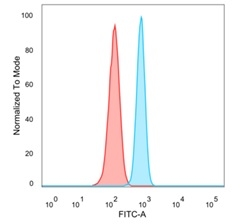
Flow Cytometric Analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. MBD3 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-MBD3-1C4) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); unstained cells (red).

SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified MBD3 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-MBD3-1C4). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.
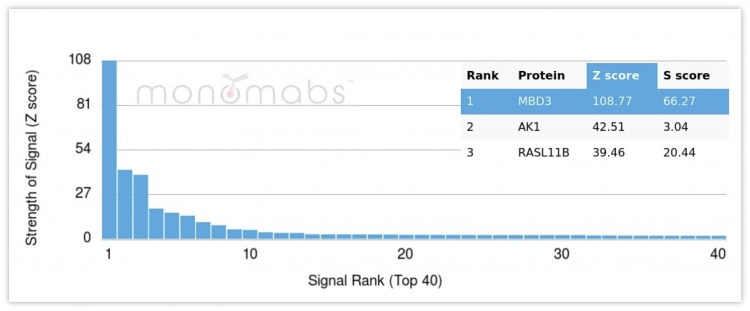
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using MBD3 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-MBD3-1C4). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
Methylation of DNA contributes to the regulation of gene transcription in both mammalian and invertebrate systems. DNA methylation predominates on cytosine residues that are present in dinucleotide motifs consisting of a 5′ cytosine followed by guanosine (CpG), and it requires the enzymatic activity of DNA methyltransferase, which results in transcriptional repression of the methylated gene. Several proteins have been identified that associate with the methyl-CpG sites; they include methyl-CpG binding protein 1 (MBD1), MBD2, MBD3, MBD4 and MeCP2. Expression of the MBD proteins is highest in somatic tissues. MBD1 binds in a context specific manner to methyl-CpG rich domains and, in turn, mediates the transcriptional inhibition that is commonly observed with DNA methylation. Similarly, MBD2 inhibits transcription of methylated genes by associating with histone deacetylase (HDAC1) within the MeCP1 repressor complex. In addition, MBD4, which is also designated MED1, associates with the mismatch repair protein MLH1 and preferentially binds to methylated cytosine residues in mismatched base pairs. MeCP2 binds tightly to chromosomes in a methylation-dependent manner and associates with a corepressor complex containing the transcriptional repressor mSin3A and histone deacetylases. MeCP2 binds tightly to chromosomes in a methylation-dependent manner and associates with a corepressor complex containing the transcriptional repressor mSin3A and histone deacetylases.
There are no reviews yet.