
Flow cytometric analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. MLX Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-MLX-1G8) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); unstained cells (red).
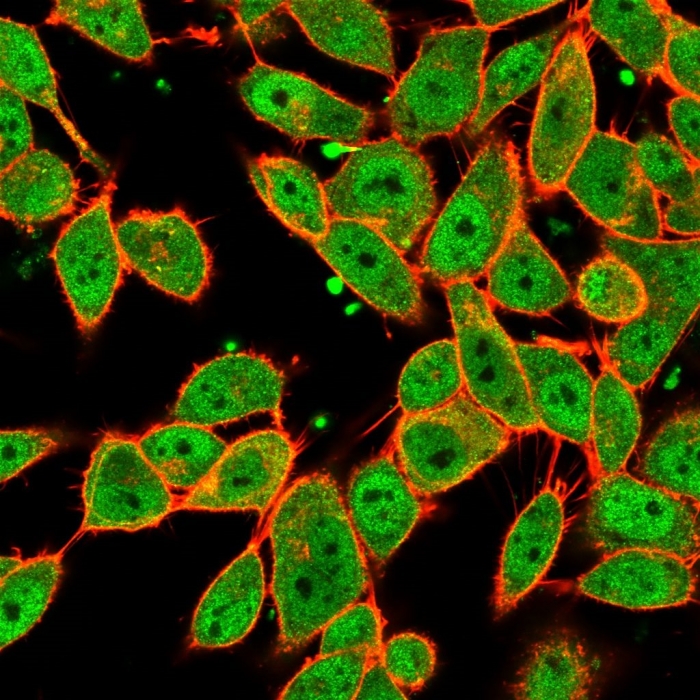
Immunofluorescence Analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. MLX Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-MLX-1G8) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (green); counterstain phalloidin (red).
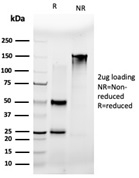
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Purified MLX Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-MLX-1G8). Confirmation of Purity and Integrity of Antibody.

Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using MLX Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-MLX-1G8). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
Max is a nuclear localized bHLH-Zip protein that forms homodimers or heterodimers with Myc family members, including Myc, Mad1, Mad3, Mad4, Mxi1 and Mnt (or Rox). These dimers bind to the E-box sequence CACGTG in order to regulate cell growth, proliferation and apoptosis. Mlx (Max-like protein X) is a bHLH-Zip protein that is structurally and functionally related to Max. Like Max, Mlx is broadly expressed in many tissues and has a long half-life. Mlx also forms homodimers or heterodimers with members of the Myc family, specifically Mad1, Mad4 and Rox, and members of the Mondo family, to repress or activate transcription from CACGTG E-boxes. MondoA forms weak homodimers and preferentially forms heterodimers with Mlx. The MondoA/Mlx complex is primarily localized to the cytoplasm, but will translocate to the nucleus in response to leptomycin B. Mlx can also dimerize with WBSCR14, a protein involved in Williams-Beuren syndrome (WBS), to repress E-box transcription, which provides further evidence that Mlx is a critical element in a transcription factor network.
There are no reviews yet.