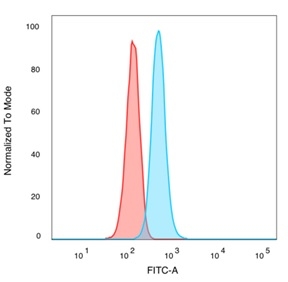
Flow Cytometric Analysis of PFA-fixed HeLa cells. TRIM24 / TIF1a Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-TRIM24-1B12) followed by goat anti-mouse IgG-CF488 (blue); isotype control (red).

Immunofluorescent Analysis of PFA-fixed MCF7 cells. TRIM24 / TIF1a Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-TRIM24-1B12) followed by IgG-CF488 (green), counterstained with phalloidin.

Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using TRIM24 / TIF1a Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (PCRP-TRIM24-1B12). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody (MAb) (in combination with a fluorescently-tagged anti-IgG secondary antibody) produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD's) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD's) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a MAb to its intended target. A MAb is considered to specific to its intended target, if the MAb has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a MAb binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that MAb to protein X is equal to 29.
TIF1伪, also known as TRIM24, mediates transcriptional events by interactions with the AF2 region of several nuclear receptors, such as the estrogen, retinoic acid and vitamin D3 receptors. TIF1伪 localizes to nuclear bodies and is thought to associate with chromatin and heterochromatin-associated factors. TIF1伪 is a member of the tripartite motif (TRIM) family. The TRIM motif includes three zinc-binding domains (RING, B-box type 1 and B-box type 2) and a coiled-coil region. The TIF1伪 gene, which maps to human chromosome 7q33, encodes two alternatively spliced transcripts. However, the full length nature of one variant has not been determined. A TIF1伪 homolog (designated bonus) has been identified in Drosophila and is associated with several genes that are implicated in the ecdysone pathway, a nuclear hormone receptor pathway required throughout Drosophila development, suggesting a conserved functional role for the protein throughout the course of evolution.
There are no reviews yet.